Key Takeaways
- Chain Abstraction: Particle Network simplifies user interaction across multiple blockchains by abstracting complex processes, improving user experience (UX).
- Universal Accounts: Offers a unified account system to interact seamlessly across different chains.
- Modular Layer 1: Built on Cosmos SDK and EVM-compatible, providing developers with flexibility and scalability.
- Cross-Chain Interoperability: Supports over 65 blockchains, including EVM and non-EVM ecosystems.
- Web3 Integration: Facilitates Web3 onboarding with account abstraction, smart wallets, and simplified login solutions.
A Refresher on Chain Abstraction
Chain abstraction is a recently developed concept in the blockchain realm designed to help eliminate the user experience (UX) challenges that fragment blockchain and Web3 application interoperability.
As a whole, chain abstraction is built on the assertion that the elimination of UX friction between blockchains should be the default to prevent the isolation of end users from front-end blockchain interaction. Essentially, the user should be unaware of the many back end processes when interacting with blockchains, mimicking the user experience of Web2.
In essence, chain abstraction is a newly-developed framework focused on the continued advancement of blockchain infrastructure that harnesses chain-connected wallets and dApps that interoperate with one another in a more streamlined manner to eliminate UX challenges.
In traditional blockchains, generally the application (think DEXs, mobile wallets etc.) gives the user a set of options during interaction. Often within traditional DeFi and blockchain systems, users struggle with UX challenges that require them to manually execute the necessary (and often awkward) steps to achieve their desired goals.
Many of these issues can be addressed via the confluence of chain abstraction and account abstraction (AA). In this respect, AA and chain abstraction combine to help streamline the swapping, bridging, and transacting of assets to eliminate the overly complex processes typically involving more cumbersome DeFi and blockchain iterations.
In today’s crypto landscape, users have continued to be susceptible to the many inefficiencies of applications (i.e., mobile and desktop apps and the like). As we touched on in our introductory blog post on chain abstraction, these include mainly poor UX and user and liquidity fragmentation.
Specifically, when a user engages with their wallet they are often unable to access the tokens they want without bridging because of siloed blockchain infrastructure. This typically includes limited cross-chain and cross-system interoperability between chains and dApps (mainly wallets and DEXs).
To help solve these inefficiencies, protocols employing chain abstraction allow for the interconnectivity of wallet balances across a wide range of blockchains through unification within a single account on top of an individual chain. They also help streamline user onboarding processes, ensuring users (especially new users) are able to manage their assets in a simpler and more effective manner.
Particle Network and other projects driving chain abstraction, orchestration, and other related constructs are focused on enabling an industry-wide shift to dramatically improve UX to help bring about mainstream adoption to massively scale the global blockchain and crypto movement.
To learn more about chain abstraction and why it plays such a vital role in blockchain and crypto’s UX-focused future, check out our comprehensive blog post on the topic.

Particle Network: A Modular L1 Designed for Chain Abstraction
Particle Network is a Layer 1 blockchain built employing the use-specific Cosmos SDK blockchain ideation framework while simultaneously leveraging a high-performance EVM execution environment.
Because Particle Network is built to serve as a chain abstraction infrastructure to help address many of the siloed limitations of current blockchain systems, the network is connected to a host of various protocols, architectural components, middleware solutions, dApps, and more.
Case and point, Particle Network initially began providing onboarding solutions that leveraged integrated account abstraction (AA) through Smart Wallet-as-a-Service (WaaS) which was eventually extended to the Bitcoin ecosystem via BTC Connect and has evolved to become chain abstraction.
By leveraging these core functionalities, Particle Network addresses user and liquidity fragmentation attributable to a growing number of independent chains, coordinating operations across networks and empowering sovereign chains with enhanced cross-chain and cross-system interoperability. In the bigger picture, the core product developed by Particle Network to solve this fragmentation is the Universal Accounts framework, which the Particle L1 exists solely to power.
Particle Network is designed to be inherently modular in nature, meaning the blockchain is fully adaptable, allowing for the integration of various modules developed for numerous customizable use-specific utilities. This means the protocol is built to be future-proof and continuously modifiable as technologies change.
Furthermore, this design allows the network to focus on specific functionalities such as chain abstraction while utilizing the highly scalable and secure advantages provided by Cosmos-focused infrastructure.
Because of Particle Network’s Cosmos SDK-enabled design, the platform is able to retain sovereignty while outsourcing many of its key functions related to verification and data availability to various ecosystem platforms (Celestia, Avail, and NearDA).
In addition, the Particle Network L1 employs the Comet-BFT consensus mechanism (formerly Tendermint) and Cosmos’ interoperoperablity-focused Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol to help facilitate cross-chain and cross-system transaction execution and connectivity to support its vision as a coordination layer at scale.
In fact, Particle leverages an independent Decentralized Messaging Network (DMN) to monitor whether UserOperations on external chains have been executed successfully to then settle the execution status on the Particle L1. The DMN itself is a decentralized network of relayer nodes responsible for monitoring external chain events and the settlement of state events.
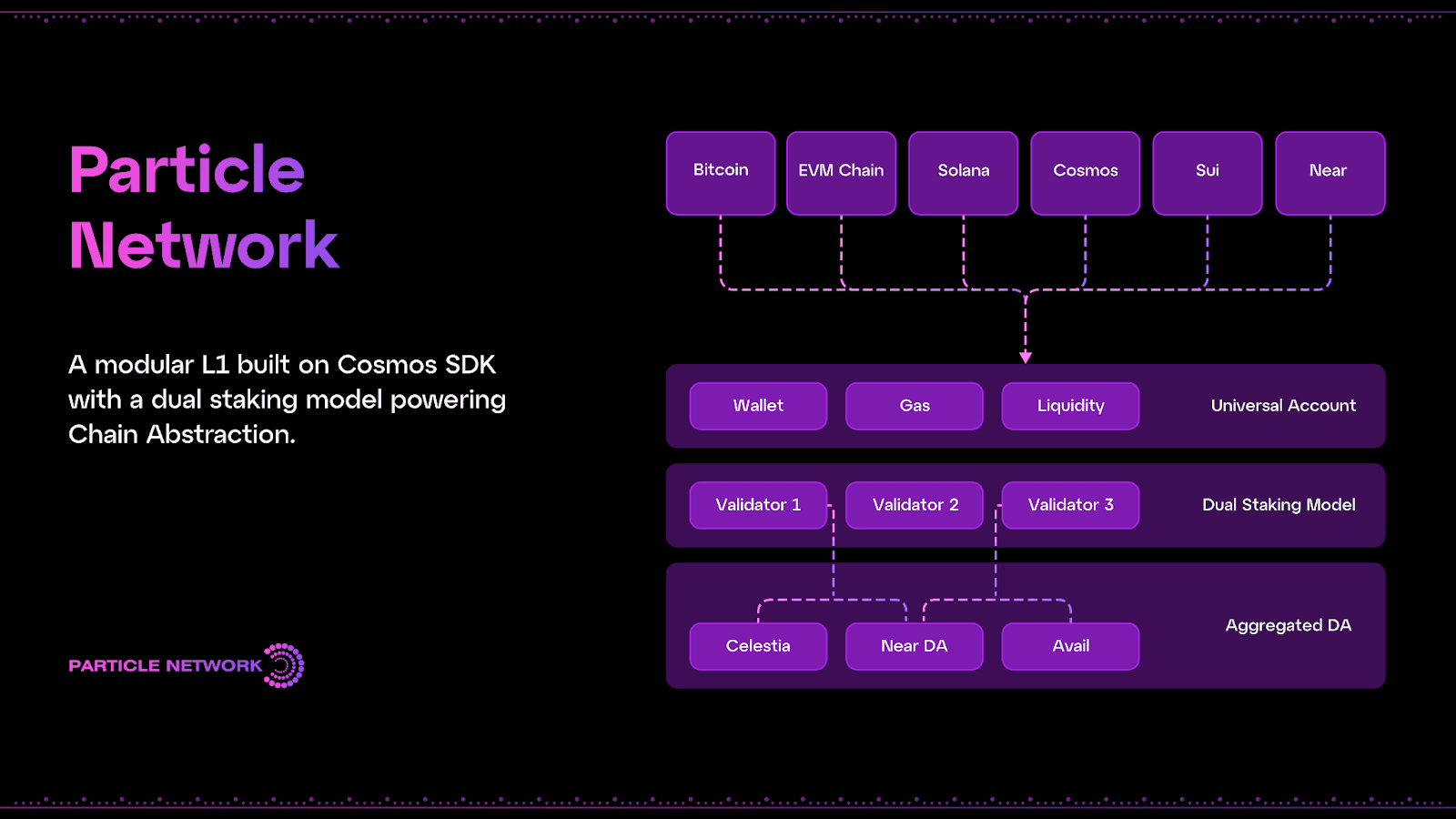
The Particle Network blockchain itself acts as a coordination layer referring to the facilitation, verification, and settlement of cross-chain transactions as well as a master keystore hub referring to cross-chain account state management.
While its support for a wide range of blockchains is continuously evolving, Particle Network's chain abstraction infrastructure is designed to connect directly to both a wide range of EVM (e.g., Ethereum, Avalanche, and others) and non-EVM chains providing strong interoperability to support both users and developers alike. In total, chain abstraction connectivity is employed amongst more than 65 chains including non-EVM blockchains like Bitcoin and Solana.
Particle Network History and Founding
Particle Network was co-founded by CEO Pengyu Wang and CTO Tao Pan in 2021.
Mr. Wang has a comprehensive background in data analysis, management, and investing which he developed through his post secondary studies and work experience at various startups and technology enterprises.
Pengyu holds a bachelor's degree in Chemistry from Tsinghua University that he completed between 2012 and 2016. He previously served as an Investment Manager at Softbank's early-stage investment fund (SAIF Partners) where he focused on sourcing, evaluating, and executing deals in the consumer internet, gaming, and blockchain sectors.
Prior to that, Mr. Wang was an analyst at China Renaissance, an investment bank that provides financial advisory services to technology companies. In addition, Wang is the CEO and co-founder of social gaming platform MiniJoy which became one of the most successful mobile gaming platforms in Southeast Asia.
Prior to becoming the CTO and a co-founder of Particle Network, Tao Pan helped develop the MiniJoy social gaming platform after successfully raising 15 million from Alibaba to help fund the project’s development. In conjunction with his co-founder, Pan studied at one of China’s most prestigious universities, Tsinghua University.
In May of 2022, Particle Network successfully raised 1.5 million in a pre-seed funding round with participation from partners such as Insignia Ventures Partners, CyberConnect, BitCoke Ventures, 7 O'Clock Capital, FSC Ventures, Monad Labs (see our Monad blog post series), and others.
Then in March 2023, the project announced it had raised 7 million via its seed investment round led by venture capital fund ABCDE with contributions from Animoca, Longhash Ventures, GSR Ventures, HashKey, and others. In addition, during April 2023, Particle Network received an undisclosed funding amount from Cobo Ventures.
Finally, in June 2024, Particle Network announced a 15 million dollar Series A funding round led by Spartan Group and Gumi Crypto, with other participants including SevenX Ventures, Morningstar Ventures, HashKey Capital, UOB Venture Management, Flow Traders, SNZ, and MH Ventures.
Particle Network Design Features
To help fulfill the ever-expanding vision that is Particle Network, independent blockchain developers building on external network’s (such as Ethereum, Avalanche, and many of largest L1s and L2s in the industry) leverage the platform’s numerous SDKs and related constructs to create amazing dApps without the heavy lifting that is often required in traditional blockchain development environments.
To accomplish this, Particle Network is built to realize an interactive user-connected Web3 model that leverages several critical elements that realize streamlined chain and account abstraction (AA). These include:
- Simplified User Experience: Chain and account abstraction help eliminate the complexity involved in managing multiple blockchains by allowing users to seamlessly interact with multiple protocols via a single interface to dramatically improve UX.
- Streamlined Development: As a developer-focused infrastructure platform, Particle Network provides a remarkably strong development environment, allowing developers to build their application-focused iterations faster and simpler than ever before.
- Enhanced Interoperability: Because of its design, Particle Network markedly increases interoperability between blockchains and systems types to promote a more collective and collaborative Web3 ecosystem.
- Increased Modularity: Particle Network’s modular design allows the platform to become more developer friendly, cross-chain compatible and interoperable with other services, while allowing for specific-product customizability.
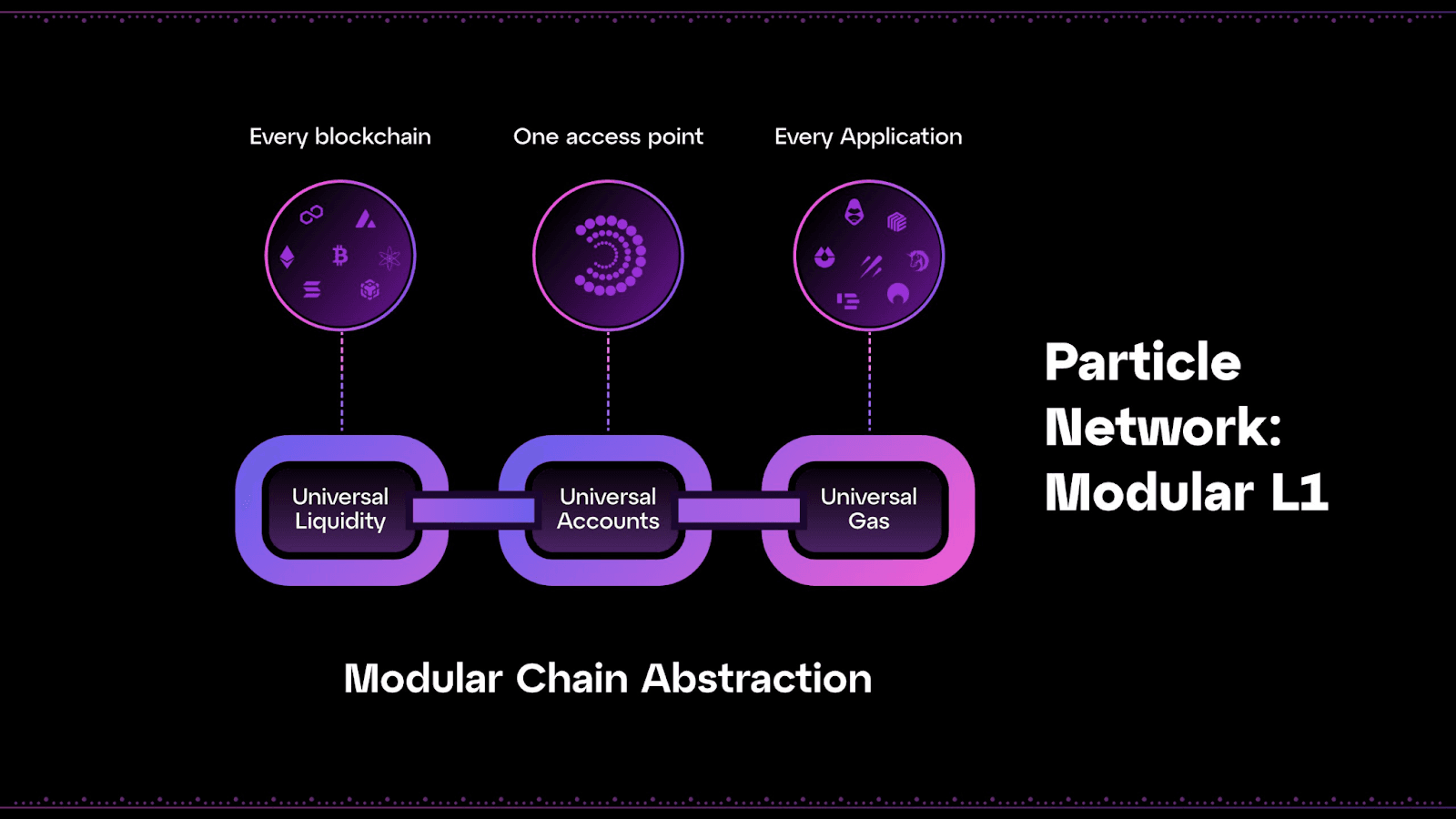
Chain Abstraction’s Many Functionalities
As a modular Cosmos-enabled L1, Particle Network furnishes chain abstraction to achieve several distinct functionalities. Therefore, the platform enables several different types of abstraction modalities, including:
- Wallet Abstraction (Universal Accounts): Wallet abstraction unifies asset storage and transactions across multiple blockchains through Particle Network‘s Universal Account via a single interaction point, user address, and balance across both EVM and non-EVM chains.
- Liquidity Abstraction (Universal Liquidity): Liquidity abstraction unifies liquidity across a wide range of blockchains via the optimistic execution of cross-chain atomic transactions and swaps, allowing users to interact with a plethora of networks without holding tokens on a specific chain.
- Gas Abstraction (Universal Gas): Gas abstraction allows users to spend any tokenized asset to pay transaction fees on a wide range of blockchains, removing the need for multi-token ownership (meaning there is no need to hold ETH, SOL, AVAX etc. to send transactions on those specific chains).
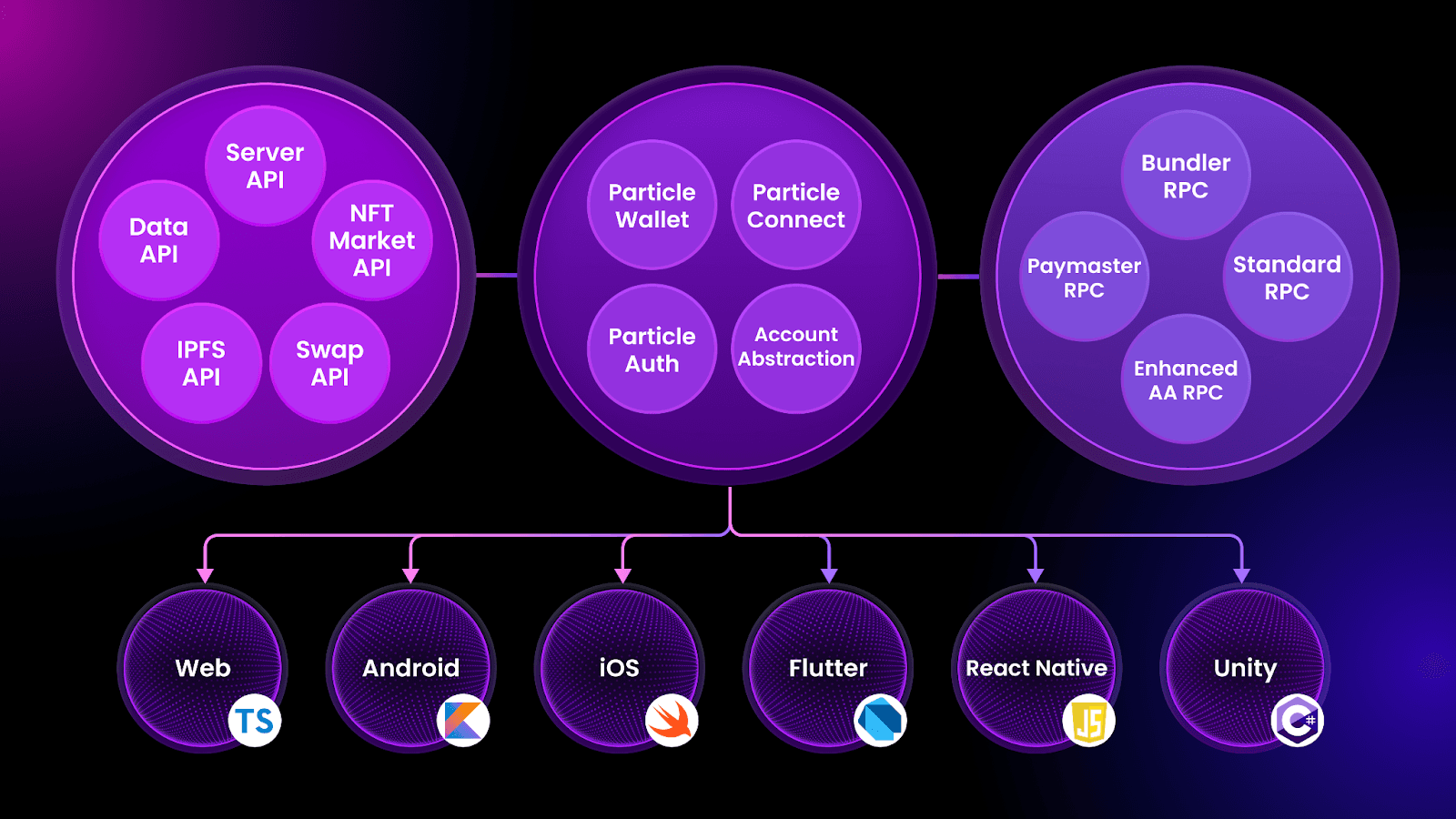
Introduction to Particle Network’s Products and Services
Now that we’ve provide a refresher on chain abstraction and touched on some of the main elements that encompass Particle Network, let’s introduce the platform’s additional product offerings covering different parts of the user experience:
- Modular Smart Wallet-as-a-Service - a Wallet-as-a-Service (WaaS) SDK enabling users to onboard to Universal Accounts using either social logins (such as Google, Twitter, etc.) or typical Web3 wallets. Developers implement an embedded wallet modal to display balances and allow for the native usage of a given wallet within an application. This service is facilitated by the two following components:
- BTC Connect - one of the industry’s very first account abstraction protocols designed to connect Bitcoin-native wallets to Bitcoin specific Layer 2 blockchains.
More importantly, Particle’s Smart WaaS and BTC Connect services act as an interpoint for wallets and users to create and access Universal Accounts. Remember, Universal Accounts, are perhaps the main fundamental component that allows Particle Network to provision the connectivity of chain abstraction and account abstraction to create an interoperable network of UX-simplified wallets and dApps.
Modular Smart Wallet-as-a-Service
Ethereum’s Externally-Owned-Account (EOA) framework is an on-chain blockchain account paradigm that gives users control over their assets. Created via private keys that provide users access to the Ethereum blockchain (and other chains), EOAs are typically used for the creation of wallets and different applications as a means to send and receive transactions. However, EOAs are not without their fair share of challenges.
Many believe that the EOA framework’s core problem is that it struggles in scenarios where advanced logic and multi-step procedures are required, both of which are critically important when it comes to development and utility of complex applications.
As a consequence, developers are often tasked with repetitive coding and inherent challenges that dictate how users interact with (or don't interact with) their dApps, as well as error susceptibility and a steep learning curve when programming.
Conversely, account abstraction (AA) and smart accounts help eliminate these challenges by allowing developers to transition users from EOAs to smart contracts as a point of interaction, execute robust multi-signature processes to dramatically enhance security, and facilitate more flexible and secure user authentication protocols inherently within the wallet’s infrastructure. For developers, this results in a fundamentally more flexible experience.
Some of the most prominent examples of dApps that face limitations due to the usage of EOAs but thrive using AA include:
- DeFi aggregators: DeFi aggregators (such as DEX aggregators and others) are capable of addressing a wide range of utilities aimed at improving UX during application interaction. DeFi aggregators allow users to interact with multiple platforms at the same time, set recurring actions (buy or sell orders etc.) within the protocol, and use numerous token types during interaction, and more. DeFi aggregation platforms that employ strong UX and seamless connectivity to fiat on- and off-ramps are greatly enhanced through account abstraction and represent a means to create completely decentralized, non-custodial, gasless platforms capable of completely replacing centralized ones.
- P2P microtransaction-powered social and media platforms: Even within low-fee environments such as L2s, EOAs make social platform interaction cumbersome and complex. Account abstraction helps simplify this abrupt approach by enabling designs that utilize peer-to-peer (P2P) microtransaction platforms that allows viewers to pay creators in proportion to their viewing time.
- Play-to-earn, gaming, and user-enabled revenue generation platforms: Account abstraction can help realize interactions and seamless transactions through Session Keys, making the technology perfectly suited for scenarios that require a continuous rapid pace of transactions. As an example, play-to-earn (P2E), and Web3 gaming experiences therefore become simpler to build while rewarding users for their time by generating in-game revenue that drives gaming and online incentivization economies.
To help improve the functionality of dApps, wallets, and the like within the industry, Particle Nework’s Smart Wallet-as-a-Service offers allows for Web3 logins and Web3 wallets to interact with applications via an embedded wallet modal which is especially useful for AA as wallets such as MetaMask and others don’t natively support smart accounts.
This is realized via an account abstraction framework that allows developers to leverage Particle’s modular design to tap into ERC-4337 AA (the original Ethereum ideation for account abstraction) within the dApp, while harnessing Particle’s Bundler Paymaster and smart account compatibilities.
Particle’s WaaS is designed to provide a simple framework that facilitates simple Web2 and Web3-friendly onboarding and wallet management within an application-embedded format. Specifically, Particle’s autonomous social sign-in model allows users to create a wallet in a few seconds as opposed to several minutes where users are required to write down a 12- or 24-word mnemonic seed phrase to secure their funds should a worst-case scenario arise.
Representing a fundamental shift in how users onboard and interact with decentralized applications (dApps), WaaS harnesses a non-custodial key management system to enable account creation through widely used social media accounts where interaction takes place via an embedded interface application.
The process of onboarding users via traditional means (such as OAuth) while ensuring on-chain interactions remain confined within a given application, as opposed to requiring extension downloads and external applications, markedly improves UX flow for end-users.
Particle’s Wallet-as-a-Service platform also ensures seamless connectivity and interoperability with numerous types of fiat on-ramps, cross-chain bridging systems, while allowing developers to more easily integrate cross-network asset swapping systems into their wallet or application should they choose to, while simultaneously providing seamless API connectivity amongst a plethora of chains.
In addition, Particle Network’s WaaS platform offers native application-embedded standalone wallet interfaces for accounts generated via social login or any accounts derived via a WalletConnect-compatible Web3 wallet.
The Particle Network wallet also allows developers to embed the platform into their standalone applications via a customizable on-screen popup to create a streamlined account management tool that is fully accessible via iOS and Android mobile applications.
In essence, Particle Wallet sits between Particle Connect and Particle Auth (see more on both below) and all three systems synergistically work together to realize account abstraction for wallet and application systems on Particle Network and other blockchains, while allowing developers to deploy wallets and applications for a wide range of environments and contexts.
Simply put, Particle Network solves problems related to onboarding, wallet management, and multi-chain friction simultaneously through the various aforementioned products.
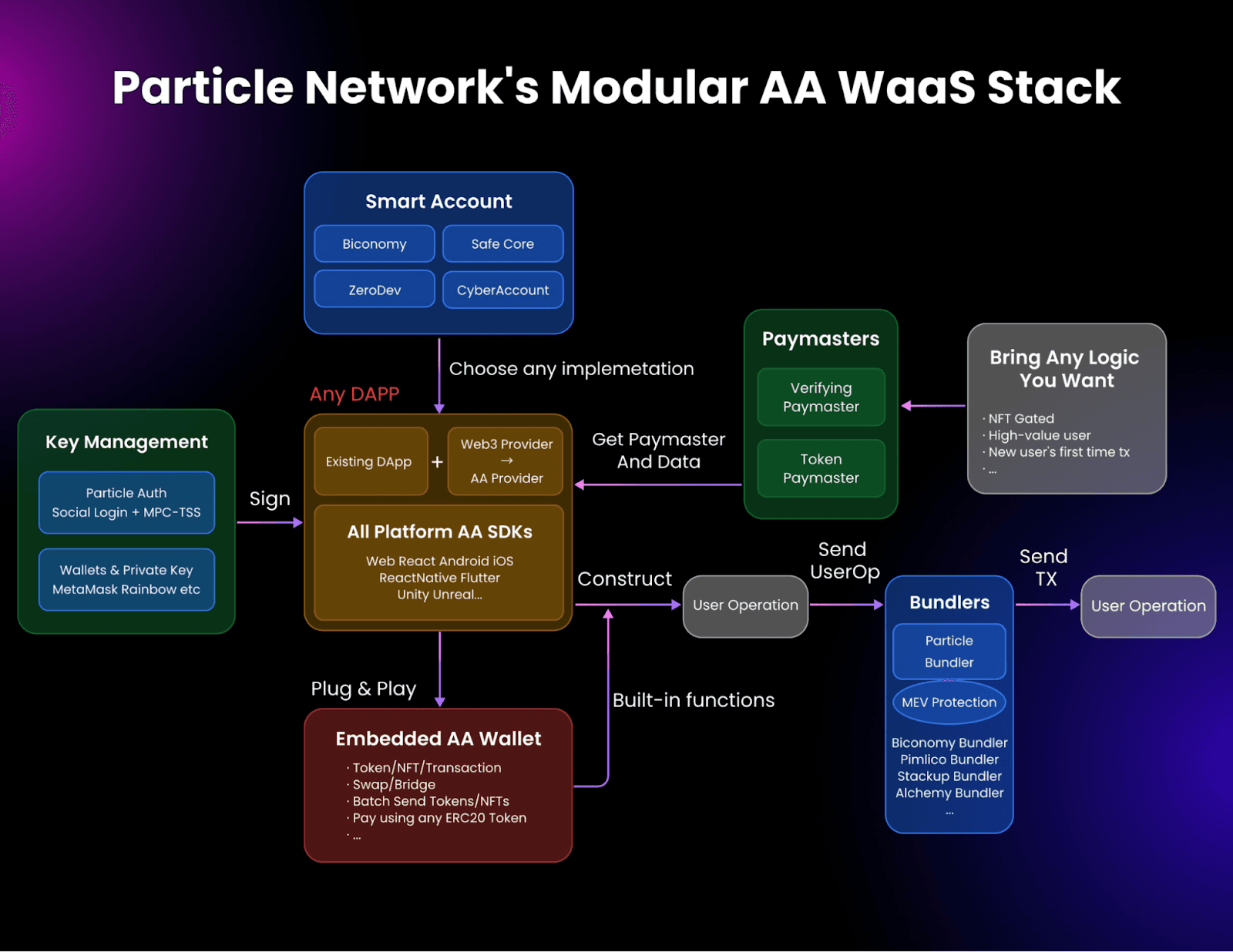
Furthermore, through account abstraction, Particle Network and its Smart WaaS framework provide a means to leverage:
Session keys - facilitates transactions that don’t require signatures as a means to streamline and simplify the transaction process and enhance UX
Paymasters - allows dApps to sponsor gas fees for users in any token type, eliminating the need to hold specific tokens just to pay gas
Bundlers - used to aggregate user actions to enable more efficient on-chain interactions, leading to reduced transaction fees and faster confirmation times, meaning better user cost-efficiency and developer performance
Particle Auth: Interoperable Wallet and Application Authentication Realized
Particle Auth is an easy-to-use non-custodial authentication infrastructure enabling Web2-friendly onboarding. Particle Auth is designed to help onboard users into Web3 via the Particle WaaS using a simple one-click Web2 adjacent interface that is fully compatible with the user’s mobile phone, email address, Google account, Twitter account, Apple ID, Facebook account, and more.
Fundamentally, the Particle Auth framework acts as the core all-in-one SDK that enables authentication and interaction within Particle WaaS and is responsible for transaction management, account information retrieval, and social login synchronicity.
To increase its far-reaching capabilities, Particle Auth is available across numerous different platforms (see below) and six different programming languages, allowing for the seamless integration of Particle’s WaaS within any Web3 application to furnish Web2-adjacent onboarding and embedded wallet interaction.
Whether via its various SDKs encompassing Web, iOS, Android, Unity, Unreal Engine, Flutter, React Native, and Cocos Creator frameworks, Particle Auth allows for streamlined and secure user application interconnectivity.
As a means to provide its state-of-the-art WaaS to different clients, Particle Auth leverages the following features:
- Rapid logins: Particle Auth provides a fast login-process similar to Web2 login frameworks to dramatically lower the barrier to entry and improve UX for wallet and app users.
- Non-custodial private key infrastructure: Particle Network provisions an MPC (Multi-Party Computation)-based TSS (Threshold Signatures Scheme) to protect wallet-holder’s private keys. By leveraging TSS, each party creates their own independent key, then with the help of the other party, they forge the vault’s lock synergistically whereby each party shapes part of the lock that corresponds to its key. By utilizing this model, the user always holds full ownership over their cryptographic key pair.
- Fully customizable user interface: Particle Auth’s UI is designed to be completely customizable, allowing developers to tailor their in-app wallet dashboards, colour schemes, and branding.
- Signature service: Particle Auth provides a full signature service that allows for the incorporation of the required specificities for sending transactions and signing messages while allowing users to view their signature data.
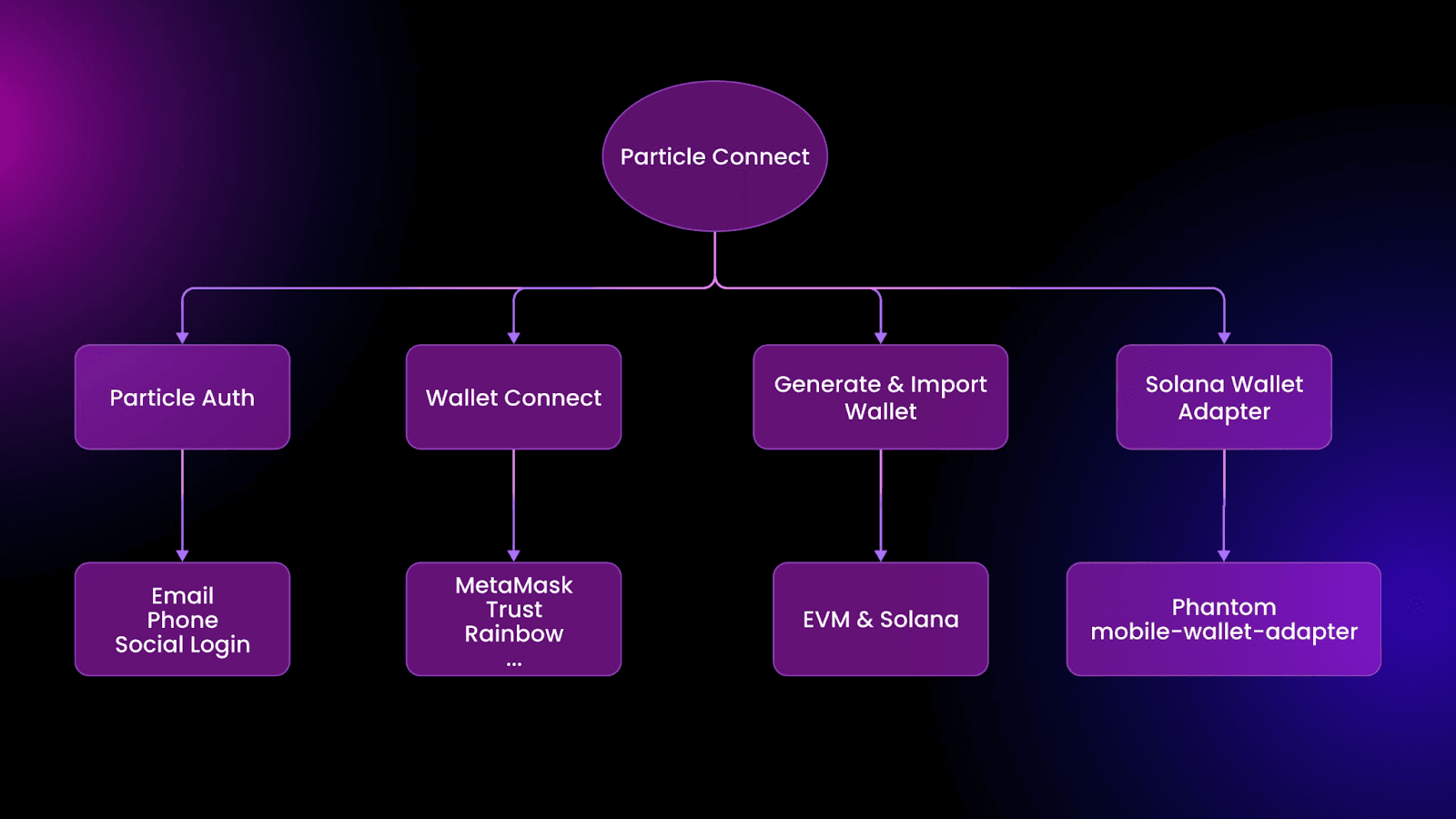
Particle Connect: Seamless Application Onboarding and Connectivity Realized
Particle Connect allows for the connection of both Web2 accounts and mainstream wallets to enhance accessibility via a unified interface.
More specifically, Particle Connect is a connection modal that allows users to onboard into applications through either Web2 logins (Particle Auth) and Web3 wallets (WalletConnect, Solana's wallet-adapter, etc.) onboarding frameworks via a cohesive custom connection modal, allowing application and blockchain developers to onboard users in a streamles, secure, and user-friendly manner.
Particle Connect’s foundational support and fundamental design lowers the initial barrier to entry within dApps by furnishing an onboarding path for a wide range of users, from Web3 natives to traditional Web2 consumers.
Particle Connect presents itself as a collection of SDKs and modules available on nearly every major platform and represents a cutting-edge connectivity layer for applications of all shapes and sizes. Some of the main wallets Particle Connect supports include: Coinbase Wallet, MetaMask, WalletConnect, Rainbow Wallet, Trust Wallet, and Phantom Wallet.

BTC Connect: Account Abstraction Wallet Connectivity for Bitcoin
With the increasing popularity of the Bitcoin ecosystem sparked by a wave of new innovations such as Ordinals, Inscriptions, and BRC-20 tokens, the introduction of numerous Layer 2 networks have emerged on Bitcoin.
However, the connectivity of the Bitcoin-EVM L2 ecosystem is sometimes considered fragmented because of the lack of interoperability between these EVM-compatible L2s and the Bitcoin L1 itself.
BTC Connect is built to solve these problems by allowing Bitcoin-native users to leverage Bitcoin wallets such as UniSat, XVerse, etc. directly on EVM-compatible Bitcoin L2s, removing the friction associated with downloading and using new wallets for the EVM ecosystem.
BTC Connect is an EVM-compatible account abstraction protocol for the Bitcoin ecosystem that enables ERC-4337 AA natively on Bitcoin L2s, allowing for the assignment and management of smart accounts directly to native Bitcoin wallets.
BTC Connect leverages a Paymaster, Bundler, and a distinct Bitcoin-specific modal (a user interface design) for coordinated use of smart accounts on EVM chains (including Merlin, BEVM, bSquared) in conjunction with Bitcoin native transactions.
More simply, BTC Connect facilitates wallet connectivity (on Bitcoin Layer 1) with UniSat, OKX, BitGet, Xverse, TokenPocket, and others, by assigning EVM-based smart accounts with a pre-specified wallet in question (acting as a signer). This service allows users to execute transactions both via smart accounts and their native Bitcoin account through the same wallet interface.
Therefore, BTC Connect helps eliminate the complexities associated with the conflicting dynamics between Layer 1 and Layer 2 accounts, allowing for the UX benefits of account abstraction, without the need for secondary interfaces like MetaMask.
This results in increased user and developer flexibility by supporting gasless transactions, batched transactions, session keys, and other related constructs.
BTC Connect’s architecture makes use of the following components:
- A connection modal used to aggregate Bitcoin wallets and facilitate direct connectivity
- An associated smart account that is easily deployed atop EVM-compatible Bitcoin L2s that have been authenticated by the initially connected Bitcoin wallet
- Account abstraction infrastructure on the corresponding L2s (including Particle’s Omnichain Paymaster, Particle Bundler etc.)
- An embedded wallet designed to control and display the associated smart account, and with it, the ability to send and receive transactions and view transactions and balances etc.
Dual Staking and Aggregated Data Availability
Aggregated Data Availability (AggDA)
As it relates to modular blockchain architectures, the most frequently outsourced component is typically Data Availability (DA). Without exception to the rule, Particle Network leverages a unique approach when it comes to the use of external DA layers.
Because of the highly data-intensive tasks related to cross-chain transaction coordination across the Particle Network ecosystem and maintaining state throughout each individual Universal Account, Particle places great importance on maximizing security and stability, while simultaneously avoiding single points of failure to ensure system resilience.
As it relates to DA, Particle Network's data availability needs are addressed through the aggregation of several main DA providers, including:
The above DA solutions bring their own uniquely distinct benefits and performance priorities. Therefore, these DA services synergistically combine to provide increased security and stability. In general, Particle harnesses either random deterministic redundancy or selective conditional publishing for each block, posting and verifying data between distinct DA layers via an Aggregated DA node set.
This specific design dramatically improves availability and stability via increased redundancy via redundant publishing, efficiency via selective publishing, and decentralization. Moreover, it provisions a distinct Aggregation of Data Availability (AggDA) model that leverages a host of providers (who are noted above).
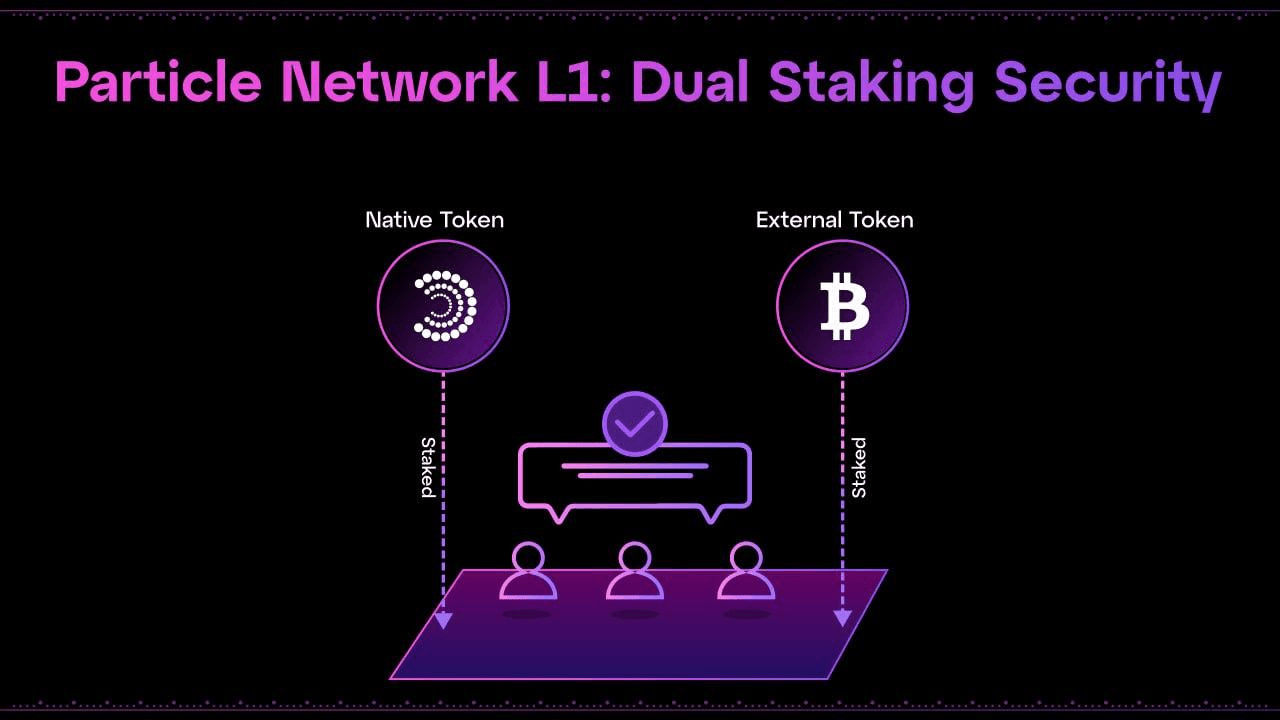
Dual Staking
By employing a comparable philosophy to AggDA, Particle Network’s consensus is built to ensure cryptoeconomic security and accessibility at its core.
As with bootstrapping any Proof of Stake (PoS) network, susceptibility to risk can be significant, primarily because of the fact that newly launched blockchain validator sets are secured to their network’s native token. This is significant because newly-launched tokens are often extremely volatile, especially in the days and weeks after mainnet launch. Unfortunately, this can dramatically affect network stability.
To help eliminate this problem, Particle Network will soon employ a dual staking model that harnesses both the cryptoeconomic security guarantees of BTC via Babylon (see our first of three blog posts on Babylon chain) and Particle's native PARTI token to ensure network security.
More specifically, this unique dual staking model makes use of two separate pools of validators: one secured by Particle’s native token, and another secure via BTC atop Babylon. It should be noted that both distinct validator sets must agree on validation separately, meaning they warrant equal consensus participation.
This model drastically reduces pressure and security dependence on Particle’s native token, instead bootstrapping the network via the cryptoeconomic security enabled through restaked BTC. It's also important to note that both AggDA and dual staking functionality will not be live on Particle’s mainnet until late 2024 or early 2025.
Resources
The information provided by DAIC, including but not limited to research, analysis, data, or other content, is offered solely for informational purposes and does not constitute investment advice, financial advice, trading advice, or any other type of advice. DAIC does not recommend the purchase, sale, or holding of any cryptocurrency or other investment.


