Bitcoin, the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, is often perceived as a static digital asset: a decentralized alternative to traditional money. But beneath the surface lies a dynamic, carefully governed protocol that continues to evolve. Over the years, Bitcoin has undergone significant upgrades to improve its scalability, transaction efficiency, and privacy. Two of the most impactful Bitcoin upgrades to date are Segregated Witness (SegWit) and Taproot, both of which have shaped Bitcoin's present and future potential.In this guide, we’ll explore the evolution of Bitcoin's protocol through upgrades like SegWit and Taproot, explain the technical innovations behind them, and offer a glimpse into future improvements including BIP-324, OP_CAT, and more.
Key Takeaways
- SegWit drastically improved Bitcoin’s scalability by introducing a new way to handle transaction signatures, effectively increasing block capacity and enabling the Lightning Network.
- Taproot enhanced privacy and smart contract capabilities with innovations like Schnorr signatures and MAST, making transactions more efficient and confidential.
- Future Bitcoin upgrades focus on privacy, programmability, and user experience, with proposals like BIP-324 (encrypted P2P), OP_CAT (advanced scripting), and BIP-119 (transaction restrictions).
- Bitcoin’s upgrade process prioritizes security and decentralization through soft forks, which maintain backward compatibility and minimize network disruption.
- Ongoing research and development from institutions like Chaincode Labs and Spiral ensures that Bitcoin continues to evolve safely, with a focus on scalability, privacy, and interoperability.
A Quick History of Bitcoin Upgrades
Bitcoin’s upgrade process involves integrating new features or changes through either a soft fork or a hard fork.
A soft fork is a backward-compatible update where non-upgraded nodes can still participate in the network, although they may not recognize new functionalities. These types of upgrades, like SegWit and Taproot, are generally preferred in Bitcoin due to the network’s conservative ethos.
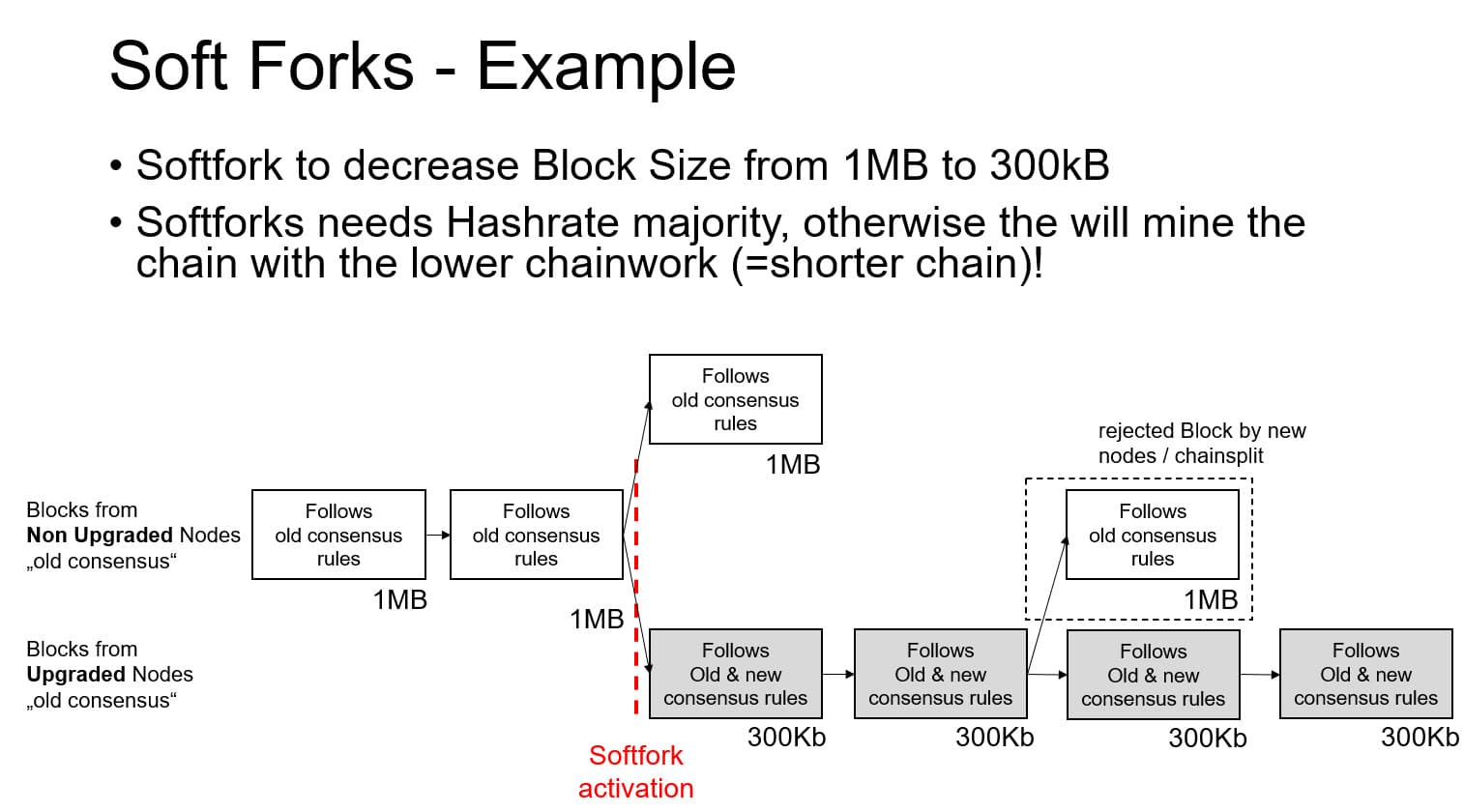
On the other hand, a hard fork introduces changes that are not backward-compatible, creating a permanent divergence unless all nodes upgrade. This type of fork was the mechanism behind the creation of Bitcoin Cash in 2017.
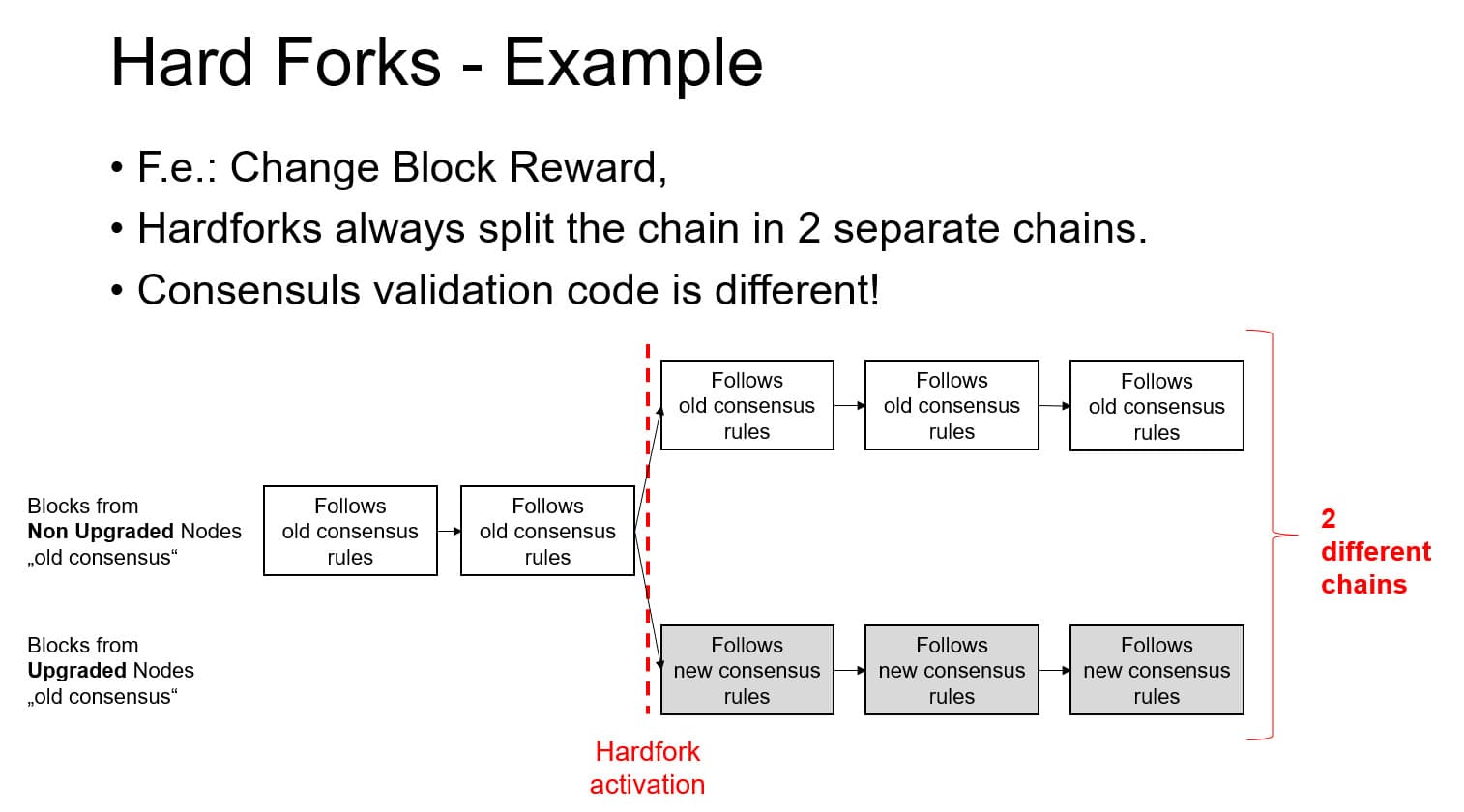
Bitcoin's upgrade path is governed through a collaborative and decentralized process. Changes are proposed through Bitcoin Improvement Proposals (BIPs), discussed by the community, tested extensively, and only then adopted if consensus is achieved. This conservative and deliberate approach ensures stability while allowing for meaningful innovation.
In the early days, Bitcoin's primary focus was establishing a secure and functional decentralized currency. As a result, foundational improvements addressed wallet usability, transaction scripts, and key management. Key milestones include:
- BIP16 (2012): Introduced Pay-to-Script-Hash (P2SH), enabling more flexible spending conditions like multisignature wallets.
- BIP32 (2012): Enabled Hierarchical Deterministic (HD) wallets, improving wallet backup and privacy.
- BIP39 and BIP44 (2013-2014): Standardized mnemonic seed phrases and wallet structure.
- BIP65 and BIP66 (2015): Tightened transaction rules and enabled time-locked Bitcoin transactions.
As Bitcoin adoption accelerated, the need for improvements in transaction throughput and network scalability became apparent. These challenges laid the groundwork for SegWit and Taproot.
What is SegWit and Why It Matters for Bitcoin Scalability
Background
By 2015, Bitcoin's 1 MB block size limit was becoming a bottleneck. The network struggled to process growing transaction volumes, leading to higher fees and slower confirmations. Transaction malleability was another issue, making it hard to build reliable second-layer solutions.
The Solution
Segregated Witness, or SegWit (BIP141), activated in August 2017, addressed these issues by separating signature data (“witness”) from the transaction data structure. This witness data is stored outside the traditional 1 MB block limit.
How it works
SegWit introduces a new metric called “block weight”. In this system, witness data counts as one-fourth the weight of non-witness data. The total block weight limit is 4 million units, which enables effective block sizes of around 1.6 MB depending on the mix of data types. This method allows significantly more transactions per block without violating the original 1 MB rule.
Benefits of SegWit:
- Fixes transaction malleability.
- Boosts block capacity.
- Reduces transaction fees.
- Enables the Lightning Network for off-chain scalability.
Today, SegWit adoption is widespread among wallets and exchanges.
Understanding Taproot: Bitcoin’s Upgrade for Privacy and Smart Contracts
Why Taproot?
Bitcoin needed better privacy and scripting functionality. Taproot, activated in November 2021, was designed to fulfill these needs through three interconnected upgrades: Schnorr Signatures, MAST, and Tapscript.
Key Innovations
- Schnorr Signatures: Enable aggregated, compact signatures for better privacy and efficiency.
- MAST (Merkelized Abstract Syntax Trees): Reveal only the executed part of a smart contract, hiding unused logic.
- Tapscript: A flexible, extensible scripting language paving the way for future upgrades.
Benefits of Taproot
- Unified transaction structure improves privacy.
- Smart contracts become cheaper and more confidential.
- Enables advanced multisig and Lightning features.
Use Cases and Adoption
- Privacy-focused wallets using MuSig2.
- More private Lightning Network channels.
- CoinJoin implementations and contract wallets with Taproot’s benefits.
Taproot’s impact is expected to grow as adoption increases.
Upcoming Bitcoin Upgrades: BIP-324, OP_CAT, and Beyond
BIP-324: Encrypted Peer Connections
Encrypts node-to-node communications using ChaCha20/Poly1305 to protect against surveillance and traffic analysis.
OP_CAT: Enabling Advanced Smart Contracts
A formerly disabled opcode (in 2010) that allows data concatenation. If reintroduced safely, it could unlock new scripting possibilities, including covenants and advanced contract templates.
Covenants and BIP-119 (CTV)
Let users restrict how and when BTC can be spent. This supports vault structures and congestion control by enforcing specific spending rules in advance.
Ark Protocol: Next-Gen Layer 2
Ark introduces ephemeral virtual UTXOs and shared pools for off-chain payments; simplifying usage without requiring direct channel management.
Ongoing R&D
- Core developers are exploring improved scalability and security.
- Organizations like Chaincode Labs and Spiral are funding critical research.
- Interoperability with other chains and privacy are top priorities.
Challenges Ahead
- Conservative governance ensures stability but slows down changes.
- Wallet and infrastructure adoption often lags behind protocol upgrades.
Despite these hurdles, Bitcoin’s upgrade path remains steady, secure, and increasingly innovative.
Frequently Asked Questions about Bitcoin Upgrades
What is SegWit in Bitcoin?
SegWit is a Bitcoin upgrade that separates signature data from transaction data to improve scalability, fix malleability, and enable the Lightning Network.
What is Taproot and how does it improve Bitcoin?
Taproot is a privacy and scripting upgrade using Schnorr signatures, MAST, and Tapscript to make transactions more efficient and confidential.
What are Bitcoin soft forks and hard forks?
Soft forks are backward-compatible upgrades. Hard forks are not and can split the blockchain if consensus isn't reached.
What upgrades are coming next to Bitcoin?
Upcoming proposals include BIP-324 for encrypted communication, OP_CAT for smart contracts, and BIP-119 for transaction constraints.
Conclusion
Bitcoin’s evolution, from SegWit and Taproot to upcoming upgrades like BIP-324, shows a protocol that prioritizes both innovation and security. These changes not only make Bitcoin faster and more scalable, but also lay the groundwork for a more private and programmable future.
The information provided by DAIC, including but not limited to research, analysis, data, or other content, is offered solely for informational purposes and does not constitute investment advice, financial advice, trading advice, or any other type of advice. DAIC does not recommend the purchase, sale, or holding of any cryptocurrency or other investment.


