Imagine a system that would monitor your transactions, be they financial or otherwise, without a controlling central authority making the decisions. Blockchain does it: a computer system that decentralizes control to a network of thousands of computers. It logs each transaction, from payments to ownership information, and locks them in cryptography before broadcasting them publicly to participants. Launched with Bitcoin, it's now driving a broader revolution, redefining how you hold assets, verify claims, and enforce agreements in a digital age. Ready to find a technology shifting trust and ownership on your terms? That's where it begins.
Key Takeaways
- Distributed Control: Blockchains doesn't have a central authority - there is a network operating the ledger in common.
- Precision Security: Securing up with cryptographic strength, stored on hundreds of nodes - your information is rock-solid.
- Direct Execution: Execute payments or contracts directly without intermediaries - your systems streamline, charges reduce.
- Real Reach: It's transforming finance, supply chains, and digital assets - things you rely on, made more efficient.
What is a Blockchain?
At its core, blockchain is a technology that lets you share and secure data without a central authority. Think of it as a digital record-keeper - a database for storing information or a ledger for tracking deals. Unlike the usual setups, blockchain spreads the control across a network of computers, or nodes, in a public or private system. This setup’s called distributed ledger technology (DLT), and it means you and other participants, not some big authority, keep it running. Nodes get digital tokens or currency for pitching in, making updates a team effort.
This system locks in every record, whether it’s a payment or a property deed, permanently and openly, so you can’t tweak it on the sly. That opens the door to swapping anything valuable, from a car to a digital artwork, with trust baked in. But what makes blockchain functional? It’s got three key traits:
First, it’s cryptographically secure. To add data, you need two keys: a public key, like your address on the network, and a private key, a personal code the system checks. Without both, you’re not able to participate.
Second, it’s all digital. Every log, every deal happens online - no paper trails or dusty filing cabinets, just a sleek, virtual ledger you access from anywhere.
Third, it’s shared across a network. Take Bitcoin’s public blockchain - anyone can set up a wallet or run a node, seeing every move.
Rewind to 2008. A mystery figure, Satoshi Nakamoto, drops Bitcoin - the first blockchain. It’s a revelation: send cash straight to someone, no bank slowing you down. In January 2009, the genesis block hits, and folks start mining—though it’s capped at just 7 transactions a second. Fast forward to 2015, and Vitalik Buterin fires up Ethereum. Suddenly, smart contracts enter the chat - automated deals that pay out when a job’s done, no middleman needed.
Since then? It’s gone wild. Chains like SUI handle 10,000 to 100,000 transactions a second, leaving traditional payment systems in the dust. Companies track veggies and supply chains. Governments test voting systems and blockchain-based CBDCs, land records. It’s not just crypto anymore, it’s a tool reshaping how we prove, pay, and follow the trail.
How Does a Blockchain Work?
Want to know what’s under the hood of blockchain? Let’s break it down.
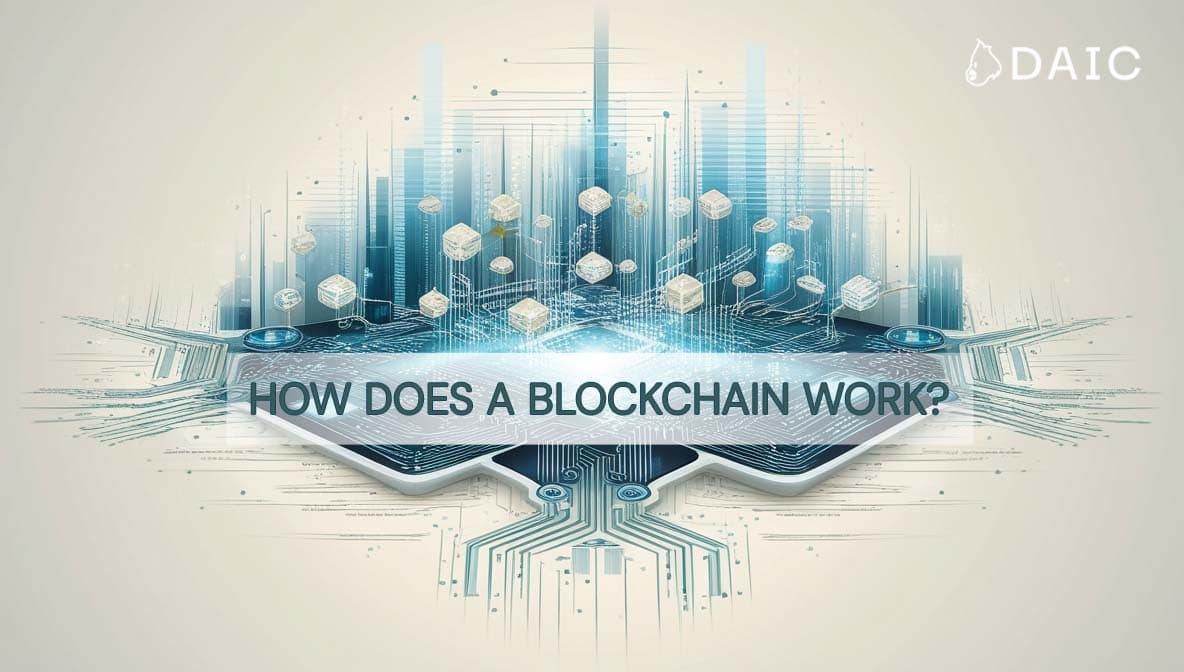
As mentioned previously, blockchain is a peer-to-peer network where nodes (computers) maintain transaction in a common database. When new information about transactions is provided it ends up in a "block" with other transactions.
Each block receives a unique cryptographic fingerprint, known as a hash. This hash is derived from the block's data and the previous block's hash, therefore it is resistant to tampering and actually encrypts the block tight.
The new blocks don't overwrite older ones, but instead link up in sequence one after another in a chain. This chain of time ensures that you are always able to trace the full record of changes - every move is irretrievably recorded, making it practically impossible to change earlier facts (an important feature known as immutability). These blocks keep accumulating endlessly, forming a digital past you can audit at any time. Every deal, from a dollar sent to an ownership transferred, stays visible and secure across the network.
Consensus is the core here—it's how blockchain stays reliable. Nodes aren't just along for the ride, they've got rigorous rules to check your moves. In proof-of-work, they race to solve math puzzles - first to figure it out confirms the deal is real. Proof-of-Stake chooses nodes that have skin in the game, tying up coins to ensure precision. Either way, it's a group decision: the majority of nodes agree, or it doesn’t fly. That’s what keeps your transactions solid, whether you’re trading currencies or tracking goods - no single player can manipulate the system.
In a public blockchain, like Bitcoin, the first node to prove a transaction’s real gets a reward. That’s “mining,” and it’s how the system pays members to keep it honest. Other networks setups rely on trusted nodes instead and reward them for their work, but the goal’s the same: your data’s locked in fair and square.
Here's an example: imagine you're buying a used laptop online. You've been burned by fakes before, so you visit a blockchain marketplace. Every laptop carries a digital identifier. Nodes on the network confirm the seller's claim before you pay, guaranteeing the laptop exists and isn't stolen. They sign off, the transaction's added to a block, and you receive an authentic machine, all thanks to that chain of trust.
Key Features of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is not just a fancy database - it's founded on some key features that set it apart from the usual tech crowd. The following are the key features that drive it, setting it apart from conventional systems.
Decentralization
Unlike the centralized setups in which there is a single entity, such as a bank with full control, blockchain uses a distributed ledger. This ledger covers a network of nodes, with each node having an identical copy of the chain and updating it together. Having no single point of failure increases resilience and builds trust with no middleman.
Immutability and Security
Security is facilitated through cryptographic methods. Transactions are secured in blocks, chained through hashes - unique identifiers that reveal any tampering. Altering a record demands reworking all subsequent blocks across all nodes, a computationally daunting feat. This ensures data, from financial records to confidential files, remains intact.
Transparency and Traceability
Transparency is inherent. Every transaction is recorded on an open ledger, accessible to all nodes. Such transparency ensures accountability, discrepancies are evident at once. In addition, the ability to trace the history of an asset makes it simple to verify and prevents dishonesty.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are automated agreements embedded in the blockchain. Programmed to execute when conditions are met. Such as “release funds upon delivery”. They eliminate third parties. This boosts efficiency and reduces costs across finance, supply chains, and beyond.
Consensus Mechanisms
Consensus algorithms, including Proof-of-Work or Proof-of-Stake, provide integrity of the ledger. It enables nodes to come to an agreement regarding valid transactions, ensuring dependability in a decentralized manner.
These features - distributed control, strong security, open records, automated agreements, and consensus - form the foundation of blockchain's value. Their real-world application follows next.
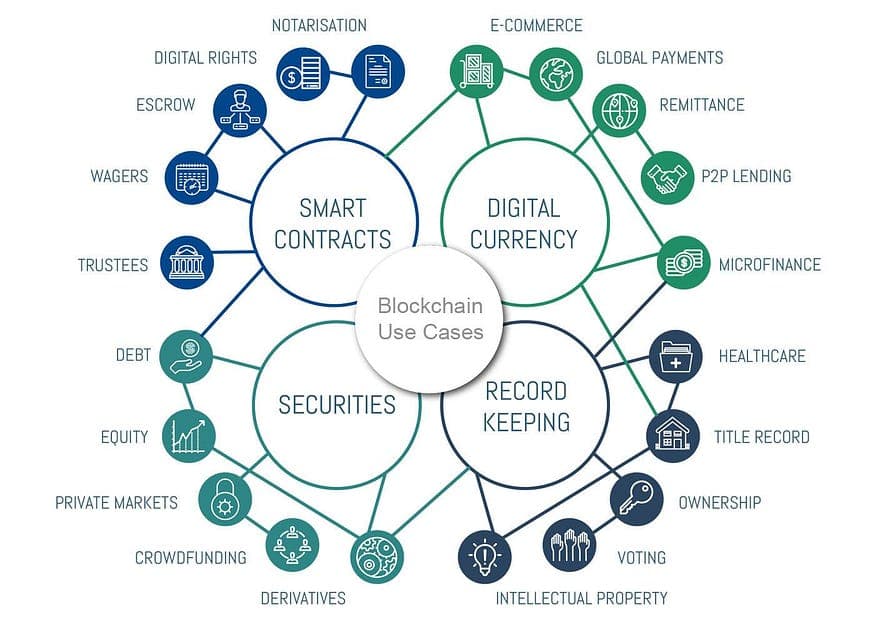
Blockchain Examples and Use Cases

So, blockchain’s not just a theory, it’s out there, doing real stuff. You’re probably wondering: where’s it actually showing up? Good question. It’s not all crypto coins and geek dreams, this tech’s quietly fixing things you deal with every day - from how your groceries get tracked to how your bank moves cash.
Crunching Data Like a Pro
Take Akash Network. Imagine a cloud computing setup where no single company, like Amazon or Google, owns the show. Akash spreads the load across a decentralized marketplace. Need to process a pile of data? It’s cheaper, tougher to crash, and every bit of usage gets logged on an unchangeable blockchain record. No fudging the numbers - your costs and resources stay crystal clear.
Healthcare That Locks Down Privacy
Now, picture your medical records. Secret Network steps in here with privacy-first smart contracts. It hosts solutions like Abakhus that allow sharing anonymized medical data for researches without spilling your personal details. Or you could control who peeks at your health file, down to the last detail. It’s secure, it’s on-chain, and it’s giving patients a say like never before.
Finance That Moves Fast
Osmosis is shaking up finance. It’s a decentralized exchange for cross-chain trading within the Cosmos ecosystem. No slow-moving brokers here, deals settle quick, and the blockchain keeps it all out in the open. Lower costs, faster action - your money works smarter.
Energy Going Green
Blockchain’s powering sustainability—two DePIN projects stand out here. First, Chain4Energy. It’s all about renewable energy trades - think solar or wind power. Every watt generated or sold gets logged on a tamper-proof ledger, clear as day. Carbon credits? Tracked too, pushing green habits with proof you can trust.
Then there’s Empower, zeroing in on eco-impact. It’s nudging things like recycling or carbon offsets - think a system that rewards you for going green, all recorded on-chain. Built to drive a circular economy, it’s live and rolling, backed by validators like DAIC.
Collectibles Fans Love
Stargaze is where NFTs, those one-of-a-kind digital treasures, take center stage. Think of it as a bustling hub for creators, from artists sketching wild designs to sports teams dropping limited-edition highlights. They’re minting what you might call “digital goodies” - think a rare illustration, a signed clip of a game-winning goal, or even a virtual ticket stub with a story. And it’s not just about making them, it’s about trading, sharing, and building something fans can’t get enough of. It’s fun, it’s fresh, and it’s connecting people in new ways.
Speedy Solutions for Almost Everything
The Sui blockchain is optimized for fast transactions with high throughput and low latency. It facilitates easy decentralized marketplaces, applications, and gaming platforms. Listing products, trades, or assessing participants are made secure through smart contracts, which provide reliability. Though its ecosystem continues to develop, its potential is evident.
Tying It Together
. Blockchain’s showing it can tackle all sorts - data processing, cash trades, even votes - stuff that’s already brushing your life, whether you notice or not. But here's the thing: this is only a glimpse at what's happening. The blockchain market’s a sprawling beast, packed with hundreds of projects beyond what we’ve covered. Think of Akash, Secret, Empower, and the rest as a handful of stars in a galaxy - bright spots, sure, but only a fraction of what’s out there. From global finance to quirky digital art, this tech’s reach keeps growing. So why’s that worth a thought? It’s not just geek toys - it’s reshaping how we trust, trade, and track the everyday.
The information provided by DAIC, including but not limited to research, analysis, data, or other content, is offered solely for informational purposes and does not constitute investment advice, financial advice, trading advice, or any other type of advice. DAIC does not recommend the purchase, sale, or holding of any cryptocurrency or other investment.


