Nillion is a decentralized, privacy-focused computing network designed to securely manage high-value data (HVD) without exposing sensitive information. By employing "blind computation," Nillion enables operations on encrypted data without decryption, utilizing privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) like multi-party computation (MPC), fully homomorphic encryption (FHE), and zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs). Built on the Cosmos SDK, Nillion ensures interoperability with various blockchain ecosystems, facilitating secure data storage, AI model training, and other applications requiring confidentiality. Its Nil Message Compute (NMC) technology allows efficient computations without inter-node communication, enhancing both security and scalability.
Key Takeaways
- Blind Computation: Nillion performs computations on encrypted data without revealing the underlying information, preserving privacy and security.
- High-Value Data Protection: The network is tailored to safeguard sensitive data such as personal identification, financial records, and medical histories, mitigating risks associated with data breaches.
- Interoperability: Leveraging the Cosmos SDK and Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) Protocol, Nillion seamlessly integrates with multiple blockchain platforms, expanding its applicability across the industry.
- Privacy-Enhancing Technologies: By incorporating MPC, FHE, and ZKPs, Nillion ensures secure data storage and processing, enabling confidential AI model training and other privacy-sensitive operations.
- Diverse Use Cases: Nillion's architecture supports applications across various sectors, including decentralized finance (DeFi), healthcare, and secure storage, by providing a robust platform for private and secure computing.
Privacy Challenges in Today's AI and Computing Landscape
Since the internet was first unleashed in 1993, the amount of data shared online has continued to increase exponentially with each passing year. Unfortunately, with the presence of so much online data, new solutions will continuously need to be developed to maintain all-important user security and privacy.
As one of the world’s most advanced technologies, the proliferation of artificial intelligence (AI) is accelerating at breakneck speed with no end in sight. This means the technology is theoretically limitless and increasingly being integrated into technologies near and far for nearly any use case imaginable.
From our text messages, to our phone calls, to our confidential medical records, our current location, our vehicles, smart homes, social media messaging history, emails, and everything in between, our all-important data is increasingly susceptible to the continuous bombardment of attack vectors of all shapes and sizes.
Personalized AI is one distinct sub sector of AI that has advanced remarkably over the past several years. Yet it is susceptible to the continuous threat of potential data breach.
Thankfully, Nillion and other technologies are designed to solve these problems. On Nillion specifically, this is realized through the creation of a specialized privacy-preserving computation network. As discussed in a recent presentation by Nillion co-founder and CMO Andrew Yeoh, Nillion is built to allow for the use of Personalized AI in a way that is secure and private so our highly sensitive data is not abused at will. To help solve the many challenges related to security and privacy of data, Nillion makes use of what it refers to as “blind computation.”

Nillion: A Newfound Privacy-Preserving Computation Network
Nillion is a decentralized, trustless, and permissionless multi-party computing network focused on solving the many challenges related to data storage, authentication, and interaction to create a seamless computing paradigm that enables true connectivity with blockchain systems, enterprises, institutions, governments, and retail users alike.
To help ensure the functioning of the Nillion’s governance, payment, and resource coordination systems, Nillion makes use of the Cosmos SDK. In many respects, the Cosmos SDK provides a versatile and robust systemization framework that represents Nillion’s vision for blind modularity, enabling the platform to dynamically adapt to network and user demands as it changes over time.
In addition, Nillion’s interconnectivity with the Cosmos SDK and the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) Protocol allows the network to be fully interoperable with blockchain ecosystems the industry over, expanding the reach and applicability of Nillion’s blind computation paradigm.
First and foremost, Nillion is built to facilitate secure and confidential data management and processing, which is critical for ensuring the integrity of numerous sensitive data processes in a number of emerging use cases. By distributing trust in a decentralized manner, Nillion reduces the risks accompanied with relying on a single entity to guarantee data security.
To gain a better understanding of Nillion's technical architecture, consider having a look at our second Nillion article.
What is High Value Data and Why is It Important?
Nillion’s privacy-focused design is built to protect our High Value Data (HVD). HVD is data that is exceptionally valuable to its owner (whether to an individual or organization), and if compromised, can be extremely detrimental. It is clear that our high value data is interwoven into the very backbone of our global society and it cannot be understated how important this data is. Examples of High Value Data include:
- Digital identity data such as your driver's license or passport
- Your entire banking history detailing everything you’ve ever purchased
- Your full medical history throughout your entire lifetime
- All your online passwords and biometric identity data
- Sexually explicit text messages between you and your partner
- Your relationship with your immediate family
- All phone calls and video calls you’ve ever participated in
Overall, Nillion is focused on decentralizing this all-important data through various forms of cryptography, both as a strategy to protect this data against a myriad of online threats, but also as a tool to help realize a more equitable data ecosystem capable of fulfilling a continually growing number of real-world applications.

The Nillion Solution
Nillion is designed as a secure computation network built to decentralize trust for high value data in a manner similar to how blockchains decentralized transactions. Traditionally, some of the greatest challenges related to the handling of high value data include:
- The availability of secure storage: In general, the process of securing high value data necessitates encryption prior to storage. Although this approach is efficient for safeguarding data at rest, it presents numerous constraints when data needs to be used or processed.
- Computing stored data without jeopardizing security: After data is successfully encrypted and stored, it is typically decrypted to allow the necessary computations to be carried out, and then re-encrypted after the fact. This 3-step cycle (involving decryption, computation, and re-encryption) creates potential security susceptibilities and can result in data handling issues.
- Realizing data management decentralization: As the premise of decentralization relates to high-value data management, data is generally distributed across a set of nodes to guarantee transparency, resiliency, and autonomy from centralized control. That said, this decentralization means it is sometimes more difficult to maintain data storage security and computational efficiency, leading to challenges obtaining consistency in security standardization and network processing, resulting in data management complications.
To address these challenges, Nillion makes use of various privacy enhancing technologies (PETs) like multi-party computation (MPC) to help securely store high value data within Nillion's peer-to-peer (P2P) node infrastructure, while simultaneously allowing computations to be independently executed upon the masked data. Ingeniously, this model removes the traditional approach of decrypting data prior to computation taking place, ultimately resulting in dramatically improved high value data security.
Nillion is designed to store permissioned secrets (i.e., high value data) and run programmable applications to perform blind computation on secrets operating atop the Nillion Network. Essentially, Nillion unveils a decentralized permissionless way of storing and processing private information and data while eliminating the pitfalls of traditional encryption, enabling the creation of a Meta Layer that turbocharges and interlinks existing blockchains, decentralized applications (dApps), and related systems using a technology called information-theoretic security (ITS).
To help realize the above goals, Nillion introduces multiple Private Enhancing Technologies (PETs) that addresses some of the most important issues plaguing privacy computing solutions. The Nillion PETnet (Private Enhancing Technology Network) is where these PETs will live, and allow for the computation and storage to take place.
Nillion is of the belief that there is no one size fits all solution, which is why the plan to incorporate multiple types of privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) such as multi-party computation (MPC), fully homomorphic encryption (FHE), and zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) to help support applications that necessitate secure and private computation via distributed data.
In traditional SMPC systems, nodes typically communicate with one another. With the Nillion Network however, nodes are not required to communicate to ensure the platform works as intended. By definition, the name Nil Message Compute is a reference to the fact that nodes don’t need to communicate with one another to achieve the desired result.
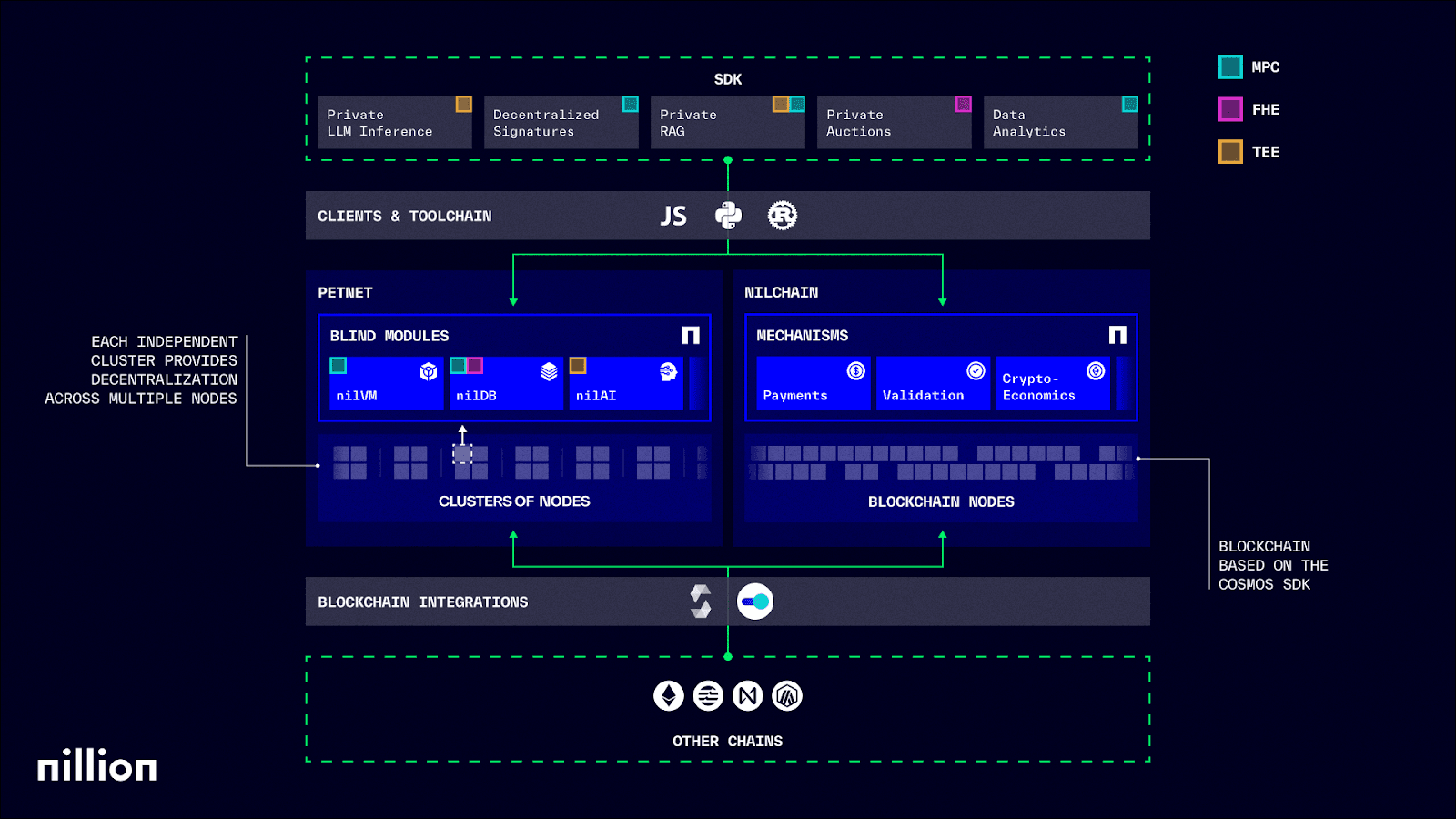
Nillion Architectural Components
Now that we have a basic overview of Nillion and how it works, let’s undercover the most important architectural elements of the Nillion platform:
Nillion Network: The Nillion Network leverages a dual network architecture that makes use of two main layers, including:
- Nilchain Nilchain helps the Nillion Network coordinate the connectivity of the network’s various components. Nilchainacts as Nillion’s execution environment and is streamlined explicitly to support intra-node use, facilitate payments, requests, storage operations, network governance, blind computation, and network resource coordination.
- Petnetthe Petnet is tasked with the orchestration of the platforms for both internal and external blockchain networks and related environments to expand access to Nillion’s storage and compute. The Petnet harnesses various privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) such as multi-party computation (MPC) to allow blind computations to compute sensitive data. Its future vision will take the form as a larger more advanced orchestration layer possessing markedly advanced capabilities.
Processing Layer - an integral component of the MPC Protocol, the processing layer allows nodes to be deployed with Nillion’s Node Development Kit (NDK) and connect to a group of clusters that distribute trust to securely process data throughout the network.
Nillion MPC Protocol - a privacy-focused protocol that utilizes multi-party computation (MPC) to ensure the cryptographically verifiable integrity of data used on the platform, the Nillion MPC Protocol enhances the capabilities of linear secret-sharing schemes (LSSS) to carry out non-linear operations that evaluate the sum of products of non-zero user inputs to facilitate secure computations for private data in a manner that doesn’t reveal individual inputs.
The Nillion SDK - Nillion’s primary software development kit and tooling system, the Nillion SDK comprises a set of tools (including CLI tools for generating node and user keys, compiling user programs, and other utilities) and libraries that allows developers to build applications via Nillion’s various privacy-enhancing technologies.
Blind apps - the default privacy-enabled application structure built to operate on the Nillion Network, blind apps leverage blind computation and numerous types or privacy-preserving technologies.
Nilion node types - various types of computers (nodes) responsible for upholding the operational integrity of the Nillion Network, these include dealer nodes, results nodes, bootnodes, and compute nodes (which can also act as relay servers atop libp2p's Circuit Relay protocol).
Nada Programming Language - a programming language designed for the development of MPC programs on the Nillion Network. The initial implementation of Nada is represented as a Python DSL (Domain Specific Language) but may take another form in its subsequent versions.
Nada AI and Nada Numpy - a state-of-the-art Machine Learning paradigm designed to integrate AI model-building via the Nada Domain Specific Language (DSL), Nada AI enables developers to import AI models into the Nillion platform for inference while harnessing the robust utility of Nada Numpy (a Python library designed for algebraic operations that allow developers to perform efficient array manipulation).

Nillion History and Founding
Founded in 2021 by CEO Alex Page, Chief Scientific Officer Miguel de Vega, and co-founder Andrew Masanto, Nillion;s mission since inception is to create a data-democratized world where our privacy and security of data is paramount and not susceptible to the overarching data-driven theft of large scale mega-conglomerates
Other important Nillion team members include Chief Technology Officer Andrei Lapets, former CTO and current technical consultant Conrad Whelan, Chief Software Architect Sergio Medina Toledo, Chief Operating Officer Mark McDermott, Chief Marketing Officer Andrew Yeoh, COO & Executive Director Claire Kelly, Head of Marketing Charlie Rogers, Chief of Staff Stefan Kende, VP of Product and AI Roel Nuyts, and Head of Finance Kevin McHugh.
In December of 2022 Nillion raised 20 million via its seed funding round. The round was led by Distributed Global, with other investors including AU21, Chapter One, OP Crypto, GSR, HashKey, Big Brain Holdings, and SALT Fund. In total, more than 150 investors participated in the raise, a strategic initiative aimed at eliminating centralization in the fundraising process.
On June 26th, 2024, Nilion finalized a community-led funding round for 20 million. This round was tailored to allow retail community members to show their support by allowing them to purchase NIL tokens (at a 400 million-dollar valuation) at a investor-friendly price prior the upcoming mainnet launch.
Then on October 30th, 2024 Nillion announced a new 25 million funding round led by Hack VC with participation from Distributed Global, HashKey, Animoca Brands, Big Brain Holdings, Ch. 1, GSR, manifold, Maelstrom, and angels such as Arthur Hayes and Meltem Demirors.

Nillion Roadmap Launch Phases
Like any computing platform nearing release, Nillion follows a distinct step-by-step development path to bring its network to the world. With Nillion in particular, its roadmap is divided into four distinct phases. These include:
Phase 1 - Genesis Sprint
The Genesis Sprint phase will be solely focused on preparing the network for mainnet launch and testing and deploying the Coordination Layer. Like most Web3-focused networks this will involve load testing the network to see how it performs basic functionalities such as wallet creation, token transfers, on-chain governance, staking, and others. Specifically, this will include the creation of the Keplr wallet, the transfer and staking of testnet tokens and downloading the Nillion SDK via Telemetry. The main objective of this stage is to obtain a better understanding of the network's possible issues and baseline performance.
Phase 2 - Catalyst Convergence
Throughout the Catalyst Convergence phase, the main objective is to continue network testing while integrating numerous other components with the network. Specifically, the Coordination layer will be integrated with the Petnet and the onboarding of external nodes and deployment of blind applications on the network will take place. This process will further decentralize the Petnet and allow for the testing of various types of cryptography and privacy-preserving technologies on the larger Nillion platform.
Phase 3 - Hardening
The Hardening phase is focused on finalizing mainnet launch. Hardening is essentially the process whereby the network’s security is markedly improved and tested and with it, full production launch is finalized. On Nillion specifically this will include production-ready secure data storage, blind computation, and the processing of real transactions to demonstrate the network’s full capabilities and resilience.
Phase 4 - The Multicluster Future
In the final Multicluster Future phase the focus will be to horizontally scale the network by introducing new clusters (groups of nodes that work together). The ultimate end goal is to create a framework that is remarkably more advanced than its initial mainnet version that allows the network to be used for an extremely large number of privacy-focused use cases. This process will allow the Nillion network to introduce a vast range of clusters that exhibit various computational and security needs based on reputation, size, performance, and hardware acceleration.
Exploring Nillion’s Use Cases
Although Nillion has numerous use cases, AI is of great significance. Specifically, Nillion helps unleash the private training and inference of AI models to establish a decentralized private alternative to centralized AI platforms. In particular, some of Nillion’s main uses related to AI include:
- AI training and inference: the process a trained machine learning model uses to draw conclusions from data
- Data sharing to earn: the monetization of personal data via AI training, inferences, and the like
- AI semantic search: a data searching technique employing the contextual meaning behind a search query to deliver more accurate results
- Personalized AI agents: autonomous intelligent systems built to perform specific tasks without human intervention
- AI synthetic data: synthetic data generated by AI algorithms while simultaneously leveraging collective model training without leaking sensitive data
Because online privacy is becoming increasingly important with each passing day, it is critical that new computing networks like Nillion build privacy-preserving technologies that complement a wide range of uses.
In addition to AI, these frameworks hold vast potential for numerous applications in a wide range of industries. Some of these include:
- Decentralized finance (DeFi): Nillion supports a wide range of privacy-focused utilities for DeFi inducing decentralized privacy-preserving order books, dark pools, and encrypted trading. Moreover, Nillion is capable of realizing additional privacy-focused DeFi applications for decentralized exchanges (DEXs), borrowing and lending platforms (money markets), derivatives solutions, and more.
- Medical and healthcare: The Nillion platform possesses the capacity to provide numerous privacy-enabled functionalities related to healthcare, genomics, and medical. These include private healthcare analytics, blind computation between healthcare datasets to preserve patient privacy, and genomics and genetics testing.
- Secure storage: Nillion is designed to host numerous types of storage for a plethora of uses including those related to digital document management and storage, quantum secure messaging, and cryptographically secure password storage.
- Decentralized Identity (DID): Nillion is capable of hosting secure and private decentralized identity solutions, while ensuring they are capable of resisting Sybil attacks via social graphs.
- Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePINs): The Nillion Network possesses the means to support cryptographically secure backends for other types of Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks such as those related to the Internet of Things (IoT), agriculture, and supply chain, among others.
In addition to the following uses detailed above, Nillion is capable of fulfilling various uses related to decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), machine learning (and deep learning) and large language models (LLMs), decentralized multi-factor authentication, private retrieval augmented generation (RAG), and trustless gaming.
Other potential applications include decentralized and private credit scoring, debt financing, intellectual property (IP), private transaction and key storage, Personalized AI, privacy-focused NFTs, decentralized trusted execution environments, custody and decentralized storage vaults, and more.
Resources
The information provided by DAIC, including but not limited to research, analysis, data, or other content, is offered solely for informational purposes and does not constitute investment advice, financial advice, trading advice, or any other type of advice. DAIC does not recommend the purchase, sale, or holding of any cryptocurrency or other investment.


