Key Takeaways
- AI-enhanced blockchain: As a network, Allora is built to integrate AI with blockchain to realize the development of decentralized, context-aware applications.
- Cosmos-based framework: Allora leverages Cosmos to achieve scalability and interoperability with additional blockchain networks and related infrastructure.
- Collaborative intelligence: The Allora platform promotes collective learning across various AI models, enhancing protocol efficiency and accuracy.
- DeFi and data solutions: Allora supports decentralized finance, data sharing, and predictive analytics, among other use-agnostic solutions.
- Privacy and security: The Allora Network harnesses zero-knowledge machine learning (zkML) to ensure secure, private AI computations.
Allora – A Thinking Network
Developed by Allora Labs, the Allora Network is a decentralized AI network built on Cosmos SDK. Allora Network’s AI is permissionless and open to any customer and to any Worker participant that meets the minimum hardware requirements. As of October 2024, Allora’s context-aware AI network is available to access on testnet.
Allora launched its Edgenet in March 2024 specifically to accommodate their strategic partnerships’ needs for evaluating the network’s capabilities. Next, Allora subsequently launched its second testnet, Testnet V2, ahead of mainnet launch. Nevertheless, Allora Labs and their strategic partners already have a number of integrations and proofs of concept deployed on testnet. Below are some examples of projects that have already been deployed either directly on Allora or via an Allora integration:
- PancakeSwap: PancakeSwap is a DEX and gaming marketplace present on many Layer 1 and Layer 2 chains including ZKsync. Recently, PancakeSwap launched an AI-Powered Prediction Market on Arbitrum where players bet with or against the Allora AI forecast ETH price movements every 10 minutes. So far, users placed over $3.8m in bets.
- RoboNet: Another DeFi actor, RoboNet is focused on the development of a DeFi platform for AI agents, with the platform harnessing Allora’s AI to ensure its agent-specific system is in working order. RoboNet went live with Pauly, its first AI Political Trading Agent with its own dedicated vault, leveraging Allora’s advanced inferences to analyze various political markets on Polymarket.
Allora Network is a new player in the decentralized AI sphere, having launched their testnet in early 2024, with it entering phase two in July. Since inception, Allora Labs joined forces with several strategic partners. For example, their most recent funding round was led by Polychain Capital, with contributions from Blockchain Capital, Framework Ventures, CoinFund, and others.
In May 2024, Allora announced they'd be providing AI solutions to the ZKsync ecosystem. For those unfamiliar, ZKsync is a major player in the Layer 2 privacy-landscape with an ecosystem of hundreds of affiliated projects. Overall, ZKsync hosts a plethora of platforms with a wide range of utilities such as Koi Finance (a DeFi protocol), Mithraeum (a strategy game), and PancakeSwap (which we initially noted above) which recently launched an AI Prediction Market on Arbitrum powered by Allora.
With its open architecture and a secure infrastructure, the Allora Network is well situated to become an important independent provider of AI inferences to systems requiring insights into the environment in which it operates. Allora’s context-awareness is well on its way to proving they are perfectly suited for many applications within the DeFi realm. The projects noted above are only a small example of numerous service-based protocols that recently integrated Allora’s AI into their products or newly-built demonstrators. That said, many more have recently moved towards potential deployment.
Notwithstanding, services with a more general data focus have also reached agreements with Allora to use the platform or provide expertise or data for model development. Strategic technology partners include: Halborn, 0xScope, Ritual, masa, and more with scopes ranging from DeFi services to database and data security applications.
In July 2024, Allora announced a partnership with Amazon Web Services (AWS), allowing ML developers to deploy worker nodes to the Allora Network via AWS Blockchain Node Runners. . To advance innovation at the intersection of AI and Web3, AWS has welcomed Allora Labs into the AWS Web3 Activate Providers program. Through this partnership, participating teams are eligible for up to $5,000 in AWS Activate Credits, which can be applied towards running Allora nodes on AWS infrastructure.

Allora’s Place in the Wider AI Sphere
Allora is at the forefront of a thriving new market for decentralized computational, ML, and AI services. Several organizations target different segments of the market for machine learning provided inferences, while many decentralized blockchain solutions have been rolled out to serve these various needs. A non-exhaustive list of blockchain projects comparable to Allora Network include:
- Bittensor: Having the most similar scope to Allora, Bittensor provides a decentralized AI network that uses subnets in a similar fashion to Allora. However, Bittensor's consensus mechanism puts a greater emphasis on running a single master model across an entire subnet, whereas Allora's focus is more geared towards utilizing multiple models within a single topic while also utilizing the superior context awareness that Forecasters in the network provide.
- Artificial Superintelligence Alliance: The Artificial Superintelligence Alliance was recently announced as a new entity representing the merger of three prominent AI projects with a common currency.
- fetch.ai: Fetch.ai is a project focusing on providing a framework for an AI economy via personalized AI agents that assist end users in their day-to-day lives.
- SingularityNET: In contrast with fetch.ai, SingularityNET is more of an application centered network. Its solutions are many, but the platform is particularly well suited for standalone applications, with them promoting a strong push for Artificial General Intelligence (AGI).
- Ocean Protocol: Ocean is a decentralized data exchange platform built for data protection with integrated AI powered data analysis and predictions.
Bittensor – Decentralized AI With Network-Wide Omniscience
Bittensor is a decentralized AI network that employs a subnet structured architecture wherein inferences are produced as a conglomeration of individual attempts at the problem by multiple workers.
In general, Bittensor’s result validation method shares similarities with Allora’s Reputer model. It should be noted that Bittensor uses a slightly different nomenclature to Allora in this regard. For example: on Bittensor, the equivalent of Allora Workers are referred to as “miners”, while the Bittensor-equivalent of Reputers are known as “validators”. It is therefore important to remember that when referring to a Bittensor validator, the node can perform either one of two radically different functions: as an AI validator, or as a blockchain validator.
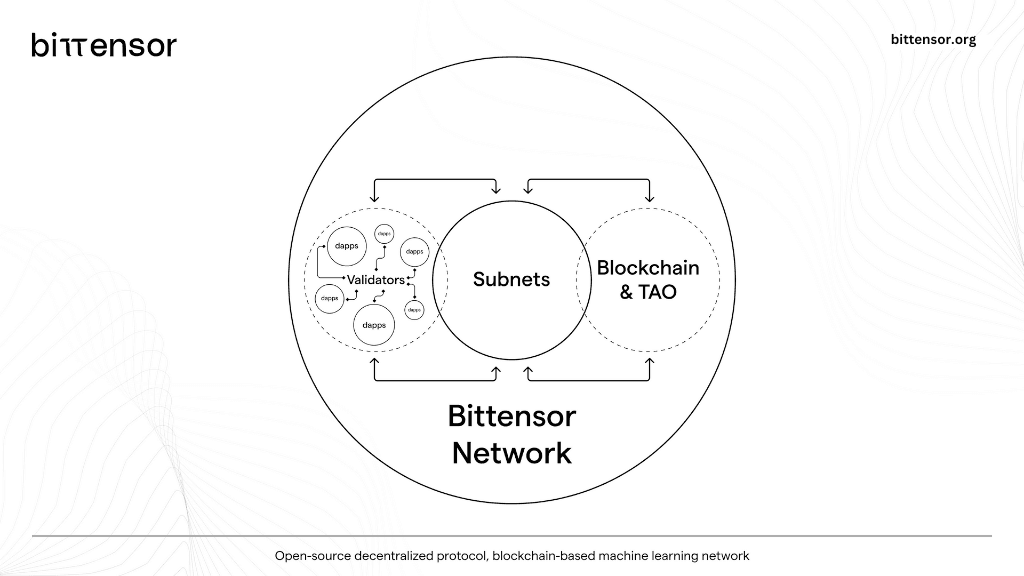
Bittensor’s approach to enhancing ML and AI performance involves compartmentalization. This strategy makes use of a diverse decentralized Mixture of Experts (MoE). The MoE model leverages the power of multiple neural networks to address complex problems, while allowing the network to choose from multiple models with deep topical knowledge but with limited scope to establish a protocol that combines these skill sets.
An example could be a request for a proposed solution to a technical problem presented in a specific language. When processing such a request, Bittensor is able to choose one set of models best suited to the technical side of the problem, but with limited language skills. On the other hand, it’s able to choose another set that doesn't possess the technical skills, albeit being experts in the requested language. This synthesized end result fulfills all end user requirements without the need to specifically train a combined model.
As the backbone of its economic system, Bittensor employs the utility of its Polkadot ecosystem-based TAO token. However, so far the protocol has not yet implemented a dedicated wallet and relies on participants using compatible wallets such as the Polkadot JS Wallet. When designing their incentive model, Bittensor opted for a strategy based on game theory that incentivizes accuracy and issues awards based on a worker’s contribution to the collective inference’s accuracy.
Furthermore, Bittensor uses a hybridized “Proof of Intelligence” system that incorporates aspects of both Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) modalities on the intelligence side of the network. In a manner similar to the way proven work within a PoW system is rewarded, a worker performs work represented as inference tasks and is rewarded based on accuracy. In general, the higher the accuracy, the higher the likelihood of being selected to add a block to the chain and being compensated with its corresponding block reward.
Like Allora, Bittensor solves the issue of siloed intelligence present in centralized schemes such as Google AI and OpenAI by leveraging inter-topic learning. A key advantage of decentralized models is that collective learning between models is made possible. Both Allora and Bittensor benefit from this approach, but what distinguishes Allora from and could give them an edge over Bittensor, is Allora’s approach for synthesis and consensus mechanisms. Through advanced synthesis mechanisms that incorporate context-awareness and forecasted loss, Allora optimizes how inferences are generated. Additionally, its consensus mechanism ensures fair reward distribution with differentiated incentives for workers, reputers, and validators, based on performance and stake.
If you’d like to read more about the pitfalls of siloed intelligence and knowledge and solutions to this problem, we’d recommend checking out our introductory blog post in this series.
Artificial Superintelligence Alliance (ASI)
The Artificial Superintelligence Alliance is a strategic alliance between three major players in the decentralized AI realm: fetch.ai (FET), SingularityNET (AGIX), and Ocean Protocol (OCEAN). As of October 2024, the alliance is in the process of migrating all participating project tokens over to the FET token which will eventually be renamed ASI. This is designed to streamline interoperability between the individualized platforms and will be of great importance to the decentralized AI sphere overall.
ASI’s founding participants represent various service-based protocols designed to fulfill different use cases for ML and AI, while being simultaneously representative of a joint vision to promote the shift towards decentralized AI. As with Allora and Bittensor, their use of permissionless computational resources lessens the influence of singular centralized entities on AI algorithms. Nonetheless, depending on the use-case, the power of interconnectivity with centralized systems such as OpenAI, Gemini, et al. is also being harnessed by ASI.
The Artificial Superintelligence Alliance proposes to merge their respective brands and technologies under the ASI banner, creating the world's largest decentralized open-source AI provider. Depending on the outcome of the merger, the above-mentioned brands may eventually become obsolete. Yet their respective competencies will undoubtedly create a formidable counterpoint to centralized AI initiatives.

Fetch.ai
Fetch.ai is built to provide personalized AI agents which take the form of entities representing compartmentalized AI powered generalized abstract user interfaces. Fetch.ai agents provide end users with a common backend-agnostic platform from which a plethora of tasks can be performed. This approach relies on agents being able to interact freely with other entities with set parameters.
These interactions can be with centralized or decentralized AI services, businesses, other agents, and more. The system is built on cryptographically verifiable trust but in a trustless environment to create an environment whereby an agent can be entrusted with performing transactions on behalf of the end user.
The network provides what fetch.ai refers to as a DeltaV interface; which is an interface built to resemble a chat interface similar to the text prompt of ChatGPT and other similar solutions. DeltaV serves as a primary tool to interact with deployed agents. Backing DeltaV is fetch.ai’s AI Engine that parses user input in natural language and passes the relevant task on to a suitable agent, who then performs the task on behalf of the user. These services are readily available via fetch.ai’s Agentverse, which is in effect a specialized Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) cloud for deploying and managing agents.
To summarize, fetch.ai is built as a close-to-home end user service that facilitates interaction with multiple services. With its unlimited interfacing allowance, fetch.ai services could potentially incorporate support for Allora based AI services in the future. That said, the system is not intended as an independent generalized AI service.
SingularityNET
On the other hand, SingularityNET is focused on creating a decentralized Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) solution open to everyone. The term AGI refers to algorithms that are able to closely mimic an intelligent thought pattern, drawing conclusions based on experience and known data. An interaction with a fully realized AGI could be made to appear as an interaction with a near-humanlike intelligence.
Additionally, SingularityNET offers an AI Marketplace where end users, in addition to being able to train their own model, have access to various existing models and services. The system has reached some maturity and exhibits a well developed economic model, which in many cases, offers a limited number of free API calls to assess a service and its applicability to the potentially desired applications required by a customer. Furthermore, SingularityNET recently integrated with PayPal to accept fiat as well as their native AGIX token (and in the near future: FET/ASI).
Like fetch.ai, SingularityNET offers access to AI agents, allowing for the incorporation of external services into a composite service. It is of course possible that with the new alliance, depending on how independent the partners remain, that SingularityNET will channel their focus towards their AGI research and agent development more towards fetch.ai collaborators.
Ocean Protocol
Ocean Protocol is the third spoke in the ASI wheel, balancing the offerings of the system overall. Ocean has developed robust protocols to ensure privacy when acting in a trustless environment. Especially as it relates to sensitive operations pertaining to personal or financial data, it is imperative to maintain security, integrity, and confidentiality of processed data at all times.
Ocean provides solutions to this problem by allowing a user to submit data to be processed off-site whilst being reassured that the private information therein remains confidential, regardless of where the processing takes place.
Once fully realized, the Artificial Superintelligence Alliance will be able to provide a compelling and comprehensive solution to customers, researchers, and developers, unencumbered by centralized AI’s potential biases. The decentralized nature of the network will allow for organic growth and, as with other comparable networks, only the adoption rate will be the final limiting factor.
To learn more about how Allora’s technical architecture works, consider reading our second blog post in our Allora series.
Regulatory Challenges for Blockchain-Enabled AI
Machine learning and artificial intelligence provide powerful new tools for data processing that have the potential to realize dramatic improvements in many aspects of society. Especially in STEM topics where rule based, but noisy data, with sometimes chaotic progression has proven difficult to model using traditional methods, ML has proven to be a game-changing technology toolkit.
Regardless, it is obvious that AI is increasingly becoming a part of our everyday lives, especially for use cases such as healthcare and finance. Particularly when sensitive information is handled, it is crucial that AI providers ensure both privacy and data integrity. Unfortunately, due to the potency of AI algorithms, several indications exist that some less savoury use-cases and even criminality could be facilitated via AI technology. This has caught the public's eye and regulation is the natural consequence.
Across the globe, newly developed AI laws are being introduced at an astounding pace, with the EU leading the way through the implementation of sweeping new regulations, going so far as to ban a host of AI cases, including some aspects of facial recognition and analysis. Other use cases have also become heavily regulated, meaning that providers of AI services will have to ensure they comply with these newly developed regulatory frameworks.
The US has adopted a more open attitude towards AI, but is still imposing new requirements on providers of the technology, including new rules to ensure AI generated content can be recognized when it is encountered.
A third major relevant market is China. Be that it may, China is somewhat nebulous when it comes to AI regulations. China has recently expressed their intent to implement regulations targeting specific uses of AI. In particular, the proposed regulations will affect applications such as: recommendation algorithms, deep synthesis technology (intended to counter issues such as deepfakes), and will mandate a registration procedure for algorithms. It remains to be seen how this will affect decentralized systems and if they will be able to operate within the Great Firewall mind you.
Despite the introduction of numerous regulations globally, Allora and other decentralized AI providers may not suffer unduly from these regulatory impositions, as they are merely the purveyors of a technology platform rather than an end user application. This means for the most part, the onus will likely end up being on the entity deploying an application to conform to regulations, as opposed to the user itself.
The Future of Decentralized Artificial Intelligence
It is obvious that decentralized networks are at the core of the future of AI and ML in general. The key to this success is to provide as accurately defined predictions as possible and a user interface that suits the application’s utility and potential user-base. Allora provides a straightforward approach whereby a Consumer will create a topic with a finite lifetime that can subsequently be queried for inferences throughout its lifecycle. Allora’s approach lends itself perfectly to applications requiring bespoke models that are integrated into larger systems.
The Allora Network is designed as a promising new approach to machine intelligence, producing inferences based not only on raw data input, but by taking into consideration context and weighing many different models against one another and the ground truth – the reality, when real world data eventually is available. Furthermore, the network is built as a permissionless fully decentralized system without a central arbiter to vet outcomes while supporting zero-knowledge technology. These mechanisms come together to power Allora’s self-improving decentralized machine intelligence network.
Allora’s next key milestone is the launch of its mainnet. In the meantime, several partners are already utilizing Allora’s advanced AI technology to enhance their products, positioning the network to secure a substantial share of the decentralized blockchain-powered AI and ML services market.
Open to anyone, Allora offers an attractive alternative to other AI and ML platforms, most of which still belong to large financial interests. The conscious decision to introduce a strict disconnect between model decisions for inference generation and the economics of running a bleeding edge service providing heavy computational tasks allows Allora to serve any customer regardless of investor sentiment. Allora Labs does not have, nor do they seek, any control over their Consumers, Workers, Reputers, or validators.
Resources
The information provided by DAIC, including but not limited to research, analysis, data, or other content, is offered solely for informational purposes and does not constitute investment advice, financial advice, trading advice, or any other type of advice. DAIC does not recommend the purchase, sale, or holding of any cryptocurrency or other investment.


