Within the growing and fast-moving DeFi ecosystem, optimizing returns has become multi-faceted. Liquid staking has indeed been one of the most critical elements of this evolution, which enables investors to generate yield with retaining capital flexibility for other uses. Decoupling the process of staking away from its traditionally illiquid nature, liquid staking empowers crypto-asset holders to maximize the utility of their holdings.This article will outline an overview of liquid staking, thereby diving deep into its benefits and risks, which form the building blocks for what is expected from the decentralized financial world in the years to come.
Key Takeaways
- Improved Flexibility: Stake your crypto without losing access to your assets.
- Boosted Returns: Collect staking rewards and participate in other DeFi.
- Unlocking Liquidity: Trade or use your staked assets as collateral at any time.
- Lower Entry Barriers: The capability of staking with much lower sums.
- Growing Ecosystem: Liquid Staking hugely adopted across major blockchains.
- DeFi Interoperability: Utilize liquid staking tokens (LSTs) in a variety of DeFi protocols.
What is Liquid Staking?
Liquid staking represents a new financial approach within the DeFi world, through which maximizing of returns is achieved by all-in-one participation in Proof of Stake (PoS) networks and the active management of staked capital. This is made possible via the issue of what is called LSTs tokens, serving as claims on the underlying staked assets, keeping them liquid and tradable.
This multi-layered design enables capital efficiency whereby investors earn staking rewards, but at the same time retain reach to a wide range of DeFi strategies that include lending, borrowing, and yield farming.
Despite the associated risks related to smart contracts and protocol vulnerabilities, Liquid staking finds wider adoption among various blockchain networks, thus it increasingly becomes more important in decentralized finance.
How Does Liquid Staking Work?
In traditional staking, once tokens are staked, they are locked up and become unusable or untradable until the staking period is over. With liquid staking, in contrast, token holders can enjoy the value of their staked assets while still being able to get their staking rewards.
Now, let us detail the whole process step by step.
- Initialization: The entire process is initiated when investors connect their digital wallets to any of the available liquid staking protocols. Due diligence is paramount in selecting a platform that should have proper security, especially clear fee structures and suitable performance.
- Asset Delegation: Further to choosing the desired amount of native tokens to be staked, the protocol involves the delegation of such assets to validators participating in the network. This forms a very integral part in terms of security and efficiency in the running of the network.
- LST Minting: It provides a 1:1 ratio of minting LSTs for those underlying assets that are staked through the protocol. These derivative tokens represent claims on the underlying staked assets, but are different in that they have liquidity and are fungible.
- Capital Deployment: Investors can be seamlessly involved in the DeFi ecosystem through LSTs. This opens all kinds of financial instruments and strategies for lending, borrowing, yield farming, or whatever else might be invented in order to maximize efficient capital deployment and potentially add returns.
- Redemption: When investors decide to unstake their assets, at that moment the process of redemption is triggered via the protocol. It includes burning the received LSTs and sends the staked tokens back along with rewards to the wallet address of the investor.
Advantages of Liquid Staking
Liquid staking lets you become both a delegator in the Pos networks and an active player within the DeFi ecosystem.
Dual Incomes: You are able to earn rewards from the very act of staking, but LS also opens a venue for your LSTs to be used in various activities within DeFi, therefore theoretically creating two potential income streams of one single asset.
Optimized Capital Efficiency: By maintaining liquidity, your capital is never idle. You can put your assets to work in multiple ways simultaneously, maximizing their earning potential.
Increased Liquidity: Unlike all traditional ways of staking, LSTs keep your staked assets available, allowing for more active portfolio management.
Multi-Platform Staking: You can diversify your staked portfolio across various platforms and protocols, thereby minimizing dependence on a single provider and reducing risk.
Lower Barriers to Entry: In many cases, liquid staking requires lower minimums than traditional staking, making it more accessible to a wider range of investors.
Liquid staking unlocks more use cases for the staked assets. In this sense, this moves the overall utility and, by extension, value for the cryptocurrencies one step further.
Risks of Liquid Staking
While liquid staking has great opportunities opened within the DeFi ecosystem, it should be underlined that the prudent investor needs to be aware of the risks involved. Primary areas that these risks can fall into include the following four:
1. Smart Contract Risk:
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Liquid staking protocols work with the help of smart contracts that are generally susceptible to a variety of potential weaknesses and coding bugs. When these are manipulated by bad actors, this often results in either the loss or theft of the staked assets themselves.
- Protocol Dependence: Intrinsic security of the staked assets is related to the robustness and security measures of the chosen liquid staking platform. Thorough due diligence into the security infrastructure and history of the platform is therefore very important.
2. Validator Risk:
- Slashing: Malicious behavior on the part of validators or failure to follow network consensus rules may result in some form of a penalty. These penalties mean that some portion of the staked assets is slashed, reducing an investor's return.
- Centralization Concerns: If the power of staking concentrates in the hands of just a few validators or is primarily dependent on one liquid staking protocol, there is a risk of centralization. That could affect the security and decentralization postulated by an underlying blockchain network.
3. Market Risk:
- Asset Volatility: By nature, LSTs obtain their value from the volatility in the price of the underlying staked asset. Major sudden fluctuations in the value of the underlying will result in impermanent loss or reduced returns.
- Liquidity Constraints: While LSTs are designed to be liquid, under certain market conditions, this may not always be the case. In such conditions, since there's much lower liquidity, you may struggle to get or convert the LST back into the original asset without great slippage or price concession.
4. Regulatory and Legal Risk:
- Evolving Regulatory Landscape: Law and regulation around the use of cryptocurrencies and DeFi continue to evolve. Changes in regulations or legal interpretations may have an adverse impact on the legality, taxation, or overall viability of liquid staking activities.
By recognizing and taking steps to mitigate these risks, investors can be confident in their liquid staking strategies and best position themselves in this expanding DeFi market.
Liquid Staking: Impact Overall Market Liquidity
Liquid staking has been one of the more influential catalysts that serve to increase liquidity within the cryptocurrency markets. According to DefiLama the total value locked in October 2024 in liquid staking is $40,681b.
These freely tradable and composable solutions offer an overall more dynamic and flexible way to participate in Proof of Stake, freeing up capital that would otherwise remain locked into traditional staking models.
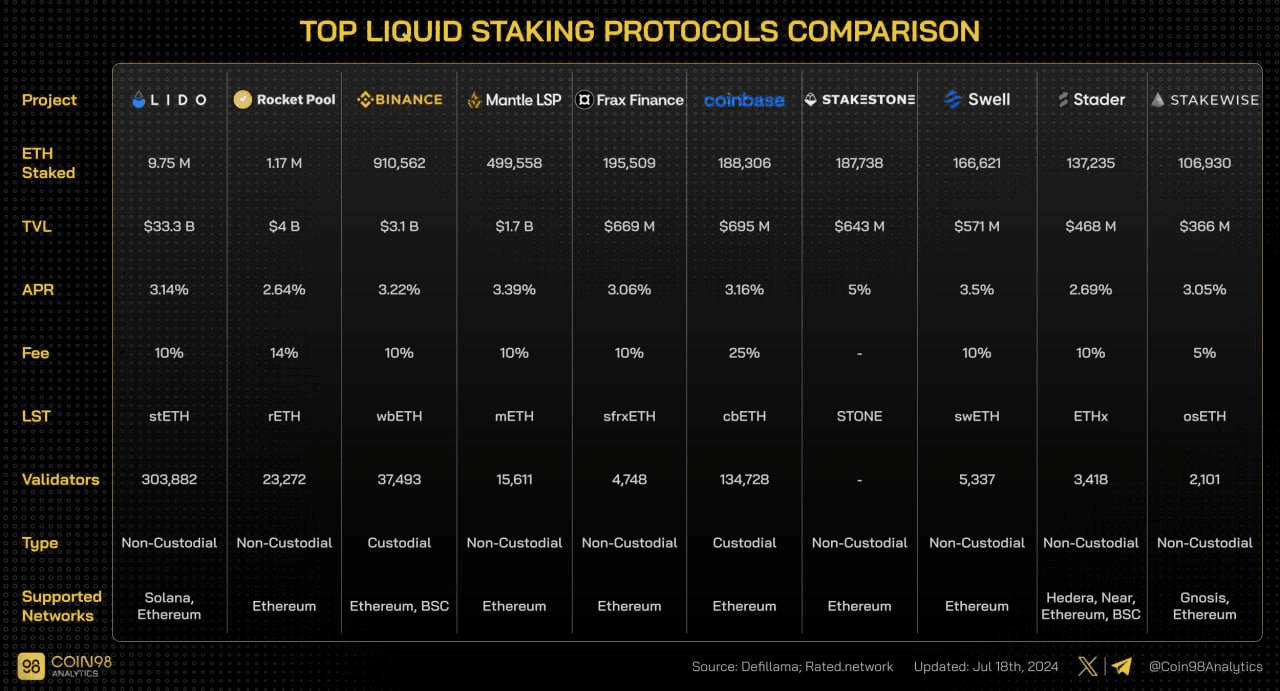
Most of the Liquid Staking protocols often do similar staking services for their users but differ in some key aspects: mainly in APR, fees, the supported network, security, etc.
As these innovative financial services become more widespread, the positive externalities for market liquidity become more pronounced, which in turn fuels the further expansion and development of the crypto space.
The information provided by DAIC, including but not limited to research, analysis, data, or other content, is offered solely for informational purposes and does not constitute investment advice, financial advice, trading advice, or any other type of advice. DAIC does not recommend the purchase, sale, or holding of any cryptocurrency or other investment.