For those just starting their journey into the world of decentralized solutions, it can be a complex maze at first. But among the many puzzles of the Web3 ecosystem, staking is especially attractive.Through many sources, you will find a simple definition - staking is a way to get rewarded for holding a certain amount of cryptocurrencies. That's true, but it's more than that!
In fact, staking is at the heart of the new generation of decentralized services. Understanding this becomes essential for anyone interested in being involved in this new digital economy.
Key Takeaways
- Active Participation: Staking is a type of active participation in the next generation financial economy.
- Reward Potential: Staking offers the potential for passive rewards in the form of additional cryptocurrency.
- Diverse Options: Rewards vary by cryptocurrency, participation rate, and platform.
- Staking Variability: Each staking approach differs in features, reward mechanisms, and user experience.
- Reward Dynamics: Actual staking rewards is a set of variables with which the investor should be well acquainted.
- Informed Decisions: Be prepared for the technicalities, rewards, and risks involved in staking.
Understanding the Basics of Staking
Beyond well-known concepts that describing easy investment opportunities for receiving profit, Staking is a core of governance mechanisms (consensuses) of decentralized networks.
In this respect, individuals who take part in staking do not remain passive observers. They rather assume an active role and become an integral part of the blockchain ecosystem, by contributing to its stability and security, and correspondingly, to its efficiency in general.
The bottom line is that staking is an intentional dedication of cryptocurrency to the network's consensus mechanism. The staked capital, in turn, serves to incentivize a holders (validators), that maintain their nodes, to be diligent as possible in their job to maintain the integrity of the blockchain. Validators, with the power of their stake, make sure that every transaction is correctly validated and added to the chain.
Since many consensus mechanisms exist, it is important to note that Staking is only possible in Proof of Stake-based networks.
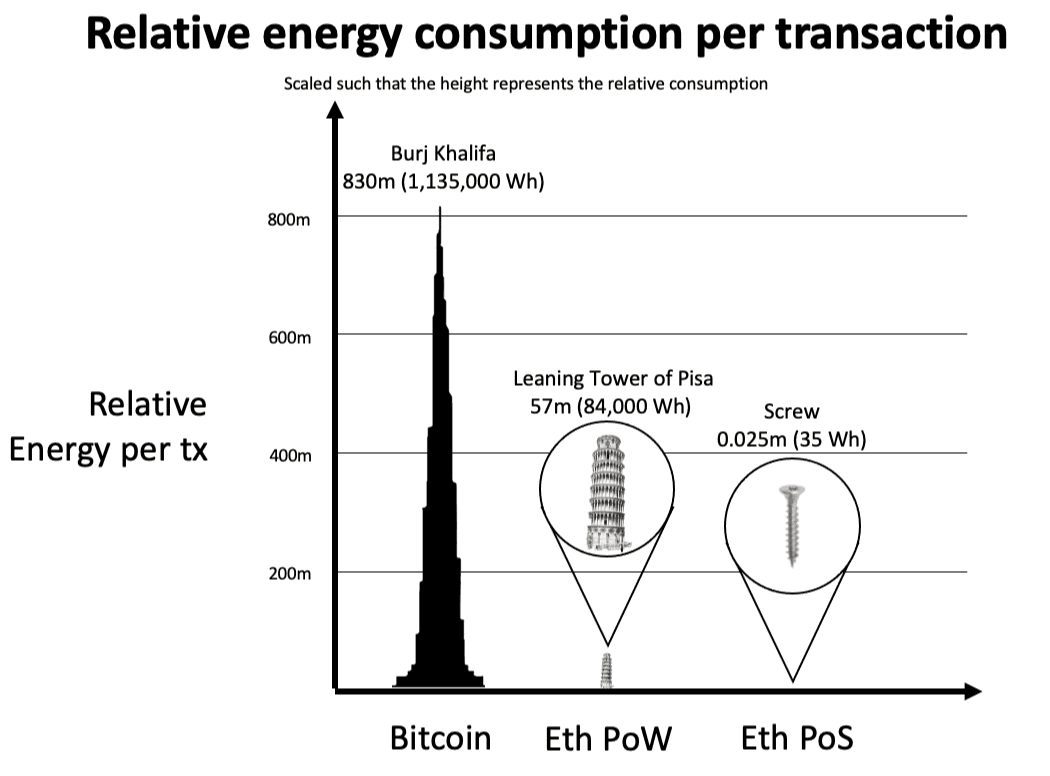
Unlike its predecessor, the power-consuming Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism (think of Bitcoin), PoS offers a paradigm shift toward an environmentally friendly approach. There is no longer a need to solve any computationally intensive puzzles, which significantly reduces energy consumption. This increasingly meets global focuses on environmental responsibility while enhancing network efficiency.
More importantly, however, staking is not only a technical feature, but this is a way for holders to directly take part in the governance of the blockchain. In accordance with their stake, users are granted voting rights to participate in important decisions with regard to network upgrades, protocol adjustments, and general decisions related to the direction in which the blockchain should evolve. In fact, really democratic, decentralized governance could be developed based on accumulated wisdom within the community about the future of the network.
The Economics of Staking
Staking lies at the very foundation of any PoS blockchain, being central to its economics. Blockchain designers are trying to find that magic formula where the network achieves high security with minimal transaction fees and strong token value at low inflation that powers growth.
As an example, high security may require higher staking rewards, the more assets staked in the blockchain, the safer it is. This can potentially lead to inflation or higher fees that may damage growth. Whereas low fees favor users, but that approach may have an adverse impact on security or higher inflation.
The intricate equilibrium forces developers to sacrifice short-term objectives in favor of the long-term aims of the blockchain. By comprehending these subtleties, we can gain insight into the economic factors that shape the PoS landscape and the strategic decisions that propel these decentralized ecosystems.
Reward Determination and Slashing
Most of the staking networks have transparent rewards system, meaning that the reward quantities in total are known upfront to all participants. In the case of the PoS blockchains, the selection of who gets to earn these rewards is at random, with staked tokens serving as the lottery ticket. The more you stake, the higher the chances of winning a share of the reward.
For instance, if an investor stakes 10 coins, and the aggregated staked amount is 100, then he has a 10% chance of being added to the network and receiving the staking reward. Since the above process repeats all the time, we are allowed to multiply the aggregate reward with the probability for calculating the expected reward.
But like every coin has two sides, so staking is not without its risks. The potential for security attacks, illegal verification, and storage failure may lead to a loss in staked tokens. Aside from probability of losing stake value or not being able to exchange their stakings, validators can also be further punished for misbehavior through a process called ‘slash’. This is the way to disincentivize actions that may cause harm to the network - for example, node downtimes or double-signing transactions.
Types of Staking
Generally, staking can be done in several ways: by running own validator node, which requires technical know-how and investment; delegating stake to some established validators, simplifying the participation but introducing reliance upon a third party; or using pooled staking to enable several individuals to combine resources and thereby increase chance to receive rewards.
Among these, the staking's contractual structure also differs: some resemble bank deposits, while others try to keep the assets as far away as possible from the provider, granting more in-person power to the stakers. Choosing the best approach depends on needs and investment objectives. For more insights into the different forms of staking, we recommend checking out our guide, "Expanding Staking Horizons: Types of Staking".
How to Start Staking
If you are not ready to run your own node, the simplest way would be to start with third-party services that support larger portfolios, such as crypto exchanges. Note that the staking reward varies based on the platform, the cryptocurrency and the participation rate. For deeper insight into the general process of staking, see our "Beginner's Guide to Staking Cryptocurrency: Everything You Need to Know".
For popular cryptocurrencies, the reward ranges from 5% to 20%, but each has its own rules and ways of giving out rewards. Some take a portion of the staking rewards, while others pass the whole amount on to the staker. The number of participants influences the staking yield: the more participants there are, the more the rewards get diluted. For further explanation, refer to "Staking FAQ: Addressing Common Questions and Concerns".
For that reason, it is recommended to keep a weather eye on the particular staking mechanism and reward structure to optimize a strategy. Once you are well aware of the variables affecting the staking reward, and you have selected a proper platform and cryptocurrency, you will be good to go to your staking journey with confidence.
The State of the Staking Industry
Staking industry has grown remarkably, with market capitalization skyrocketing to over $500 billion. Driving the surge is the growing adoption of PoS blockchains and their lucrative rewards that are attracting increasing participation.
Innovations such as liquid staking make access to staking even more democratized by providing flexible ways to earn rewards without necessarily locking up assets. This type of staking provides derivative tokens, ensuring flexibility and liquidity while participating in the consensus of the network.
Going forward, the staking landscape will continue to evolve. With more blockchains turning to the PoS model, allowing stakers a wider range of options, we can expect more network diversification. Clarity in regulations will also make the operation environment much safer and more predictable for participants. Eventually, continuous innovation within staking mechanisms and deeper integrations within DeFi are supposed to rewrite the grounds of staking by pushing the space toward even further growth and adoption.
The information provided by DAIC, including but not limited to research, analysis, data, or other content, is offered solely for informational purposes and does not constitute investment advice, financial advice, trading advice, or any other type of advice. DAIC does not recommend the purchase, sale, or holding of any cryptocurrency or other investment.


