Key Takeaways
- Decentralized Staking: Milkyway Protocol offers a decentralized and secure staking platform for various digital assets.
- Interoperability: Supports multiple blockchains, allowing cross-chain staking and rewards.
- Yield Optimization: Provides users with tools to optimize staking rewards through automated strategies.
- Governance: Token holders can vote on protocol changes, ensuring community-driven governance.
- Sustainability: Designed to maintain long-term rewards and staking stability.
What is Staking?
For those unfamiliar, staking is a financial incentivization mechanism that compliments the technical architecture, governance, and economic systems of Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchains.
In order to operate, PoS chains make use of staking, whereby users are required to “stake” or bond (deposit) their tokens within a validator node that operates within the inner workings of a blockchain network in confluence with its underlying consensus mechanism.
In exchange for depositing their tokens within a validator, users are given a predetermined tokenized annual reward rate known as an annualized percentage yield (APY). Not only are depositors (generally called delegates or nominators) given a recurring dividend for the duration they stake, they help strengthen the network’s overall security.
Relatedly, the more total stake within a blockchain network, the more secure it becomes long-term, meaning the more users globally stake within a specific chain, the less likely the network becomes susceptible to a host of attack vectors.
In addition, staking also allows network participants to contribute to on-chain governance and additional mechanisms that help guide the long-term development trajectory of a PoS chain.
This is critically important because it helps allow decision-making processes to be conducted in an equitable and decentralized manner, enabling new blockchain startups to be governed by a larger overall community as opposed to a few all-important project founders.
In addition to validators that are tasked with the security-inducing mechanisms required to run a blockchain network, various types of staking (such as liquid staking and others) can be carried out through various types of staking protocols such as MilkyWay and others.
What is Liquid Staking and Restaking?
Now that we are familiar with the general concept of staking, let’s introduce two of the most well-known staking types in today’s crypto landscape:
- Liquid staking: Liquid staking is a staking model that allows users to stake their assets (such as TIA and others) while receiving a liquid staking token (LST) (such as milkTIA) that allows them to interact with various DeFi iterations on numerous in-ecosystem protocols (including the platform hosting the user’s initially deposited assets and others), while allowing users to withdraw their deposited assets without a restrictive withdrawal waiting period.
- Restaking: Restaking is a paradigm that employs many of the same principles as liquid staking, with the main difference being that the model allows users to support distinct service-based protocols (such as Actively Validated Services (AVSs) on EigenLayer or MilkyWay) that employ a shared security model that dramatically improves protocol security for all participants.
MilkyWay: A Modular Paradigm for Celestia Staking
MilkyWay is a modular staking platform that provides both liquid staking and restaking serviceability for its users.
In the larger picture, MilkyWay is designed to unlock the potential of modularity by creating an infrastructure built for the development of various types of staking models. As a reminder, modularity is a design construct that allows for the interchangeability of various modules akin to a system of blockchain-focused lego blocks.
Although generally, the exchangeability of various modules in blockchain systems is interconnected to a particular use case or use cases, within MilkyWay specifically, the framework allows for the the iteration of numerous staking infrastructures. This modular design allows the network to abstract away the many complexities that developers typically face during the protocol bootstrapping phase, allowing newly developed platforms a better overall chance of long-term success.
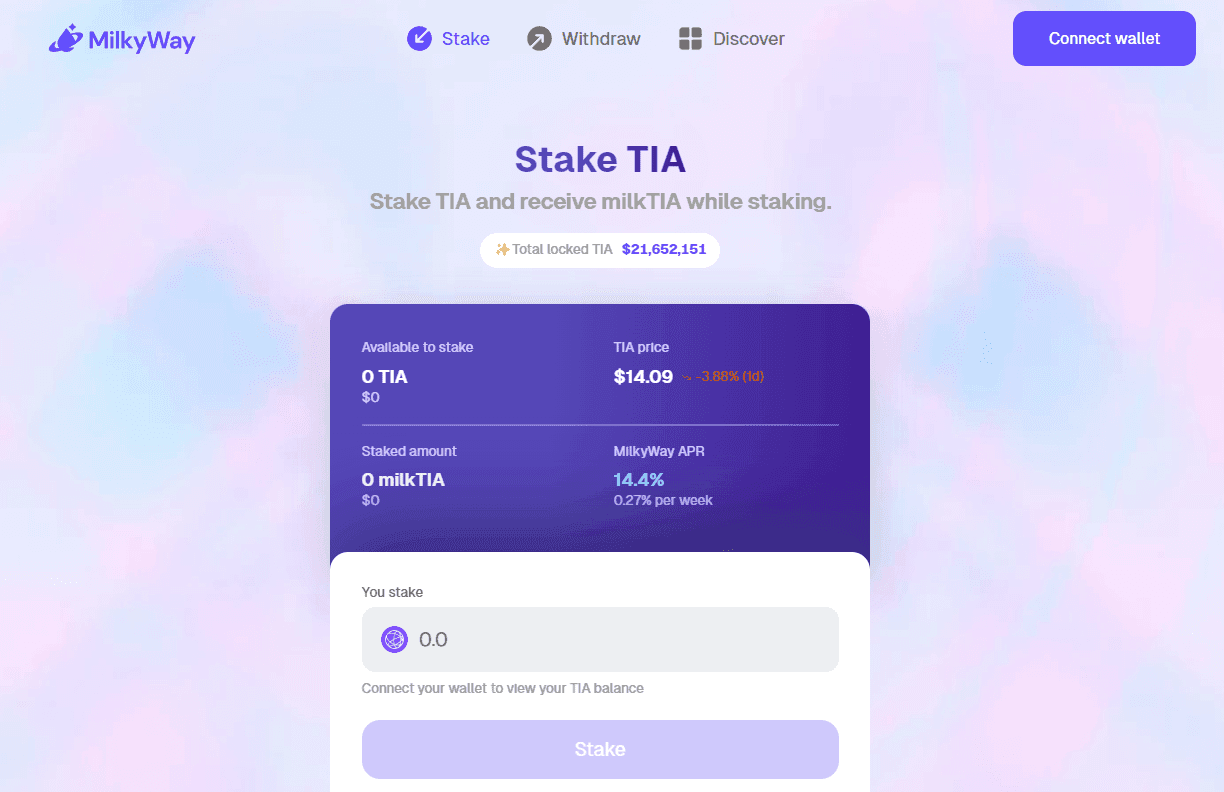
In October of last year, MilkyWay began the development of its liquid staking platform on Celestia and launched its protocol in December. This began with Phase 1 of the platform’s end-to-end staking paradigm as a mechanism to empower TIA holders through a framework that allows stakers to unlock their staked positions to enable participatory action within various DeFi platforms.
Essentially, this process allows stakers on MilkyWay to lock their native TIA assets within the protocol in exchange for milkTIA (a liquid staking receipt token redeemable for TIA).
Like any liquid staking protocol, this process allows users to receive incentivized token rewards (in the form of TIA), while also enabling the use of milkTIA within various DeFi constructs such as decentralized money markets, perpetual swap exchanges, traditional DEXs, and others.
To guarantee the liquidity access numerous Cosmos, Celestia, and Initia ecosystem exchanges, money markets, and related protocols, the mikTIA token continues to be regularly listed to support access to a plethora of related platforms.
This is vital to ensure the continued success of the MilkyWay platform because it provides accessibility to milkTIA amongst a large number of users within the crypto ecosystem. One of the most prominent DEXs milkTIA is listed on is Osmosis, the most used decentralized exchange within the Cosmos ecosystem.

Liquid Staking Benefits
As a reminder, liquid staking allows users to stake native tokens without having to adhere to the inability to withdraw their assets should they choose to. Instead, liquid staking providers leverage a liquid receipt token in exchange for their initially deposited assets, which can then be redeemed instantaneously at a moments notice.
On MilkyWay and other restaking platforms, the benefits of restaking are multi-fold and include the following:
- Liquidity and Flexibility: The process of liquid staking allows user assets to remain fully liquid at all times, meaning that no waiting period is required if a user wishes to withdraw their staked assets should they elect to. In addition, users also retain the flexibility of using their assets in a multitude of ways within a host of DeFi protocols.
- Improved Network Security: The security of liquid staking protocols typically improves exponentially as more assets are deposited within.
- Capital Efficiency: Traditional staking models allow users to earn incentivized staking rewards in exchange for securing an underlying L1. In contrast, liquid staking dramatically increases capital efficiency by allowing users to earn additional yields across a plethora of DeFi avenues.
Basic Overview of Potential milkTIA Uses
Within the MilkyWay protocol, the milkTIA liquid staking asset exhibits a vast range of potential applications within the Cosmos, Celestia, Ethereum, and Initia ecosystems.
Some of these include: as market liquidity for a host of decentralized exchanges (for the trading and exchangeability within various DEXs) and money markets (lending collateral, initially deposited stake, milkTIA pools, perpetual trading etc.).
As of this writing, for example, MilkTIA is listed within a plethora of decentralized exchanges (DEXs), L2s, DeFi platforms, and other protocol types. These include: Osmosis, Dymension, Camelot, Demex, Levana, Margined, Mars, and soon Initia and its many newly developed protocols and services.
Additionally, milkTIA is used within the Celestia ecosystem as payment for blobspace and applications developed atop the Celestia network. More particularly, chains and applications operating on Celestia employ the utilities of TIA to access Celestia’s data availability services through the submission of the PayForBlobs gas fee payment mechanism.
Though yet to be determined, there is a good chance that similar mechanisms will soon leverage milkTIA for similar processes. Should this payment and gas payment serviceability be rolled out, it would support increased chain security and utility for the milkTIA asset, ultimately eliminating the incentive to forgo staking to ensure TIA availability for data availability and transactional gas fee payment.
Upon Initia mainnet launch, it seems inevitable that many of these same utilities will be realized on Initia itself. It should be noted that the above applications represent a fraction of the potential applications for the token as more uses are developed atop MilkyWay in the years and months ahead.
MilkyWay Restaking
In recent weeks, the MilkyWay platform initiated the commencement of Phase 2 in its development process, with the main product offering being a multi-asset restaking protocol.
As a refresher, restaking is a specialized staking mechanism that allows users to harness liquid restaking tokens in a manner similar to the liquid staking process, albeit with one main caveat; restaking is built to help eliminate fragmented trust models in blockchain systems by improving the many efficiencies related to crypto-economic security in blockchains today.
Restaking represents a novel framework that incorporates an underlying validation mechanism to help achieve consensus on a blockchain network. Comparable to how PoS addresses many inefficiencies in PoW systems related to energy usage and protocol efficiency, restaking allows newly developed platforms susceptible to some of the challenges that may be encountered in current PoS systems such as those related to liquidity bootstrapping and security vulnerability susceptibility.
To help address these issues, the core concept of restaking revolves around sharing economic security via a pooled security model, whereby token holders (i.e., restakers) are able to deposit their assets (LRTs) through restaking processes to secure the network’s integrity well beyond their native chain, resulting in improved efficiency and security for all involved.

Case and point, along with MilkyWay’s liquid staking offering within the Celestia ecosystem, MilkyWay will soon offer a restaking paradigm within the Intia ecosystem (check out our 3-part Initia blog series) after the Initia mainnet launches later this year.
This means that MilkyWay will furnish a dual-pronged-ecosystem designed to provide two main service offerings (i.e., liquid staking and restaking) that address two distinct market segments.
Once restaking is implemented atop MilkyWay, LST assets will gain increased utility by providing liquidity to external blockchains (via AVSs; more on these below) and serving as a collateralization asset for restaking services. Furthermore, in time, the scope of restaking will extend well beyond milk-LST to incorporate a host of additional liquid staking assets.
Relatedly, MilkyWay’s restaking paradigm provides three main network participants a marketplace that allows them to achieve their end goals they ultimately cannot achieve on their own.
These include: 1.) stakers, who want to leverage the network as a means to accrue tokenized rewards but don't have the means to run and maintain their own infrastructure; 2.) operators, who want to maximize the use of their validation infrastructure but need stakers to receive payment for their services; and 3.) protocol builders or Actively Validated Services (AVSs), who don’t want to undergo the complexities involved with protocol development at the infrastructure level, but have a need for economic security and operational support.
Let’s look the main network participants that furnish the restaking model on MilkyWay:
- Actively Validated Services - applications or protocols that piggyback security and cryptographic trust via a larger blockchain infrastructure system (in this case MilkyWay and Initia) while offering a plethora of services to the larger network. Essentially, Actively Validated Services are middleware service modules that require distributed validation semantics for verification (i.e., they need support from a validation operator to provide serviceability to the larger network). Examples of AVSs include bridges, sidechains, oracle networks, trusted execution environments (TEEs), consensus protocols, data availability (DA) layers, virtual machines, and others.
- Restakers - protocol users who deposit their assets via the MilkyWay platform to provide economic security to the larger network in exchange for recurring incentivized staking rewards. By depositing their milkTIA, milkINIT tokens within the platform, users can be given a liquid restaking token via AVSs like Initia (essentially a LRT or LST) that represents the user's initially deposited stake, with the option to redeem their initially deposited asset upon redemption.
- Operators - independent entities (companies or individuals) responsible for running AVS software on top of MilkyWay and Initia. Fundamentally, operators are specialized validators that provide validation for different middleware service modules (AVSs) so they are able to carry out their intended tasks and services. Additionally, operators are designed to optimize AVSs and increase capital efficiency by reducing their own operational costs, while simultaneously being rewarded for their efforts.
Although the restaking framework offers an extremely innovative and capital efficient model for blockchain systems that remarkably improves security and the accessibility of a wide range of services, the model does come with some potential challenges and risks.
One of the main problems with restaking is that it can be a complex undertaking for users new to blockchain and crypto. The fact is that restaking relies on extremely complex smart contract infrastructure and bugs can exist within these contracts no matter the care taken during auditing processes.
Moreover, the model also offers the potentiality for contagion risk. For example, let's say an operator is slashed (penalized) by an AVS for not following the parameters of the protocol, the restaking slashing penalty could reverberate across the entire staking ecosystem, potentially lowering the value of the overall restaking pool and even compromising the security of other AVSs operating on the network.
Despite these risks, by provisioning the accessibility of restaking serviceability into the larger crypto ecosystem, protocols such as MilkyWay and others help ensure the continued growth of modularity and increased customer yields industry-wide.
The Future of The MilkWay Protocol
MilkWay is one of many protocols in blockchain and crypto that represents an innovative approach to eliminating the inefficiencies of traditional staking practices in blockchain systems.
With its initial focus on liquid staking, and now with the upcoming introduction of restaking, the platform offers a plethora of mechanisms that allow users to increase the yield they generate on their staked assets. The end result is a network that offers increased capital efficiency and a host of additional benefits including ecosystem-wide security improvements and minimally abated accessibility to increased yield via the utility of DeFi-focused LSTs and LRTs.
In addition, with Initia’s upcoming mainnet launch, MilkyWay will act as an infrastructure service provider that will garner continuously expanding utility from the protocol’s and user’s that build their service-specific iterations atop the network. Because MilkyWay is designed to be modular in nature, the protocol exhibits the architecture needed to allow for the introduction of newly developed staking paradigms and various utilities as the network's size increases.
Although the platform is in its infancy, MilkyWay represents a strong solution to the inefficiencies of traditional staking solutions via its offering of liquid staking and retaking services within both the Celestia and Initia ecosystems. The platform's extremely innovative and ever-evolving approach bodes well for increased user adoption moving forward.
The information provided by DAIC, including but not limited to research, analysis, data, or other content, is offered solely for informational purposes and does not constitute investment advice, financial advice, trading advice, or any other type of advice. DAIC does not recommend the purchase, sale, or holding of any cryptocurrency or other investment.


