Key Takeaways
- Restaking with Bitcoin: Babylon enables decentralized Bitcoin staking within the Cosmos ecosystem, enhancing PoS security.
- Cosmos Partnerships: Integrates with major Cosmos projects like Osmosis, Injective, and Stride, boosting ecosystem interoperability.
- Cross-Chain Expansion: Aims to extend beyond Cosmos to support Ethereum and other blockchain ecosystems.
- Security Model: Leverages Bitcoin’s security guarantees to improve blockchain resilience.
- Future Roadmap: Upcoming mainnet launch in 2024 with testnets already active.
Introduction to the Babylon Ecosystem
Babylon boasts a growing ecosystem of Cosmos-specific projects that contribute to the overall utility of Babylon chain and the greater Cosmos network.
Babylon exhibits a host of partnerships with a wide range of Cosmos ecosystem projects focused on numerous utilities and market segments. These include gaming, zero-knowledge and privacy, decentralized physical infrastructure networks (DePINs), decentralized storage, decentralized cloud computing, rollups-as-a-service, and other use-specific iterations.
In addition, like most blockchain ecosystems, Babylon chain and Cosmos are heavily focused on the decentralized finance (DeFi) niche, boasting many separate protocols furnishing various offerings such as decentralized money markets, liquid staking platforms, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), and more.
In time, the Babylon project will surely expand to numerous additional chains outside of the Cosmos ecosystem, but for now, Babylon chain is focused on securing PoS Cosmos chains to support the many use cases these various protocols are developing.
Learn more about Bablyon’s in our introduction blog post:
Babylon Chain (BABY): The Bridge to PoS Staking on Bitcoin
A Refresher on Restaking
Babylon accomplishes increased Proof of Stake chain security via a newfound paradigm of DeFi called restaking. Although Babylon chain supports both staking and restaking, Babylon makes use of bitcoin (BTC) restaking utilities by piggybacking Bitcoin’s security to support independent Cosmos chains.
Restaking is significant because it increases security for the network’s it supports, providing security-as-a-service, while simultaneously rewarding stakers for their efforts.
Retaking essentially allows users to leverage their capital two-fold, first by staking their original token (i.e, bitcoin, ether (ETH), and others), to then receive specialized liquid restaking tokens (LRTs) that can then be used within the specific chain’s DeFi ecosystem.
For those interested in obtaining a better overview of how Babylon works, consider reading our article on Babylon's technical architecture.
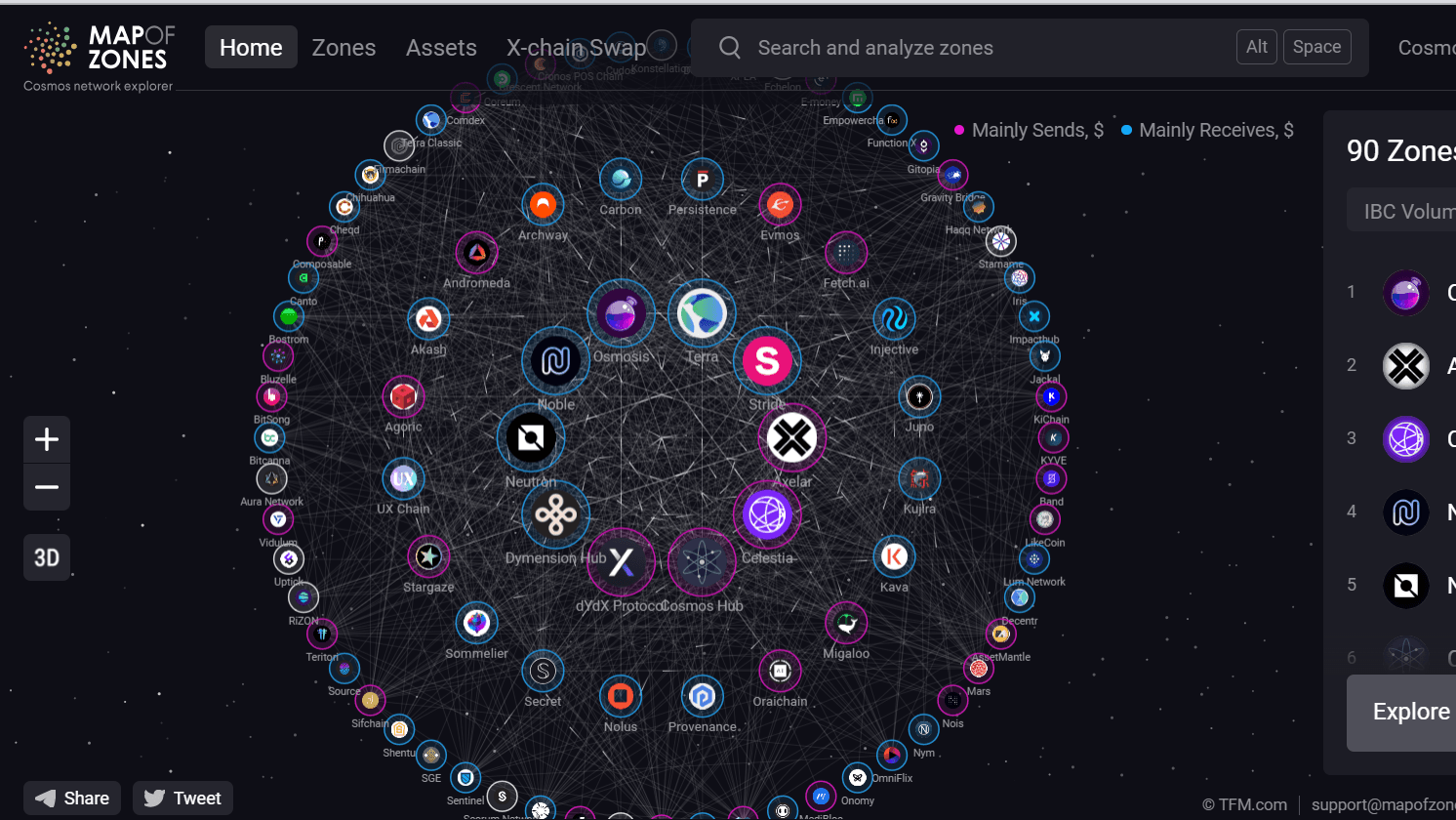
Babylon Chain’s Cosmos Ecosystem Partners
Babylon chain possesses strong partnerships and relationships with a large number of Cosmos-specific blockchains.
In many ways this is based on Babylon’s shared Bitcoin security model whereby restakers earn rewards for their efforts, while simultaneously improving the security of chains operating on the larger Cosmos network.
More specifically, the following Cosmos projects have integrated their platforms in various capacities with Babylon chain:
- Osmosis - the most prominent decentralized exchange (DEX) built atop the Cosmos network, Osmosis features swapping, trading, staking, and full integration with Cosmos’ Keplr wallet.
- Injective protocol - a smart contract platform featuring EVM and Cosmos-IBC compatibility and its own DeFi focused ecosystem composed of various dApps and independent protocols.
- Sei Network - an EVM-compatible network focused on highly scalable DeFi within the Cosmos and Ethereum ecosystems.
- Akash Network - a decentralized open cloud marketplace and DePIN infrastructure platform
- Kava Network - a DeFi chain similar to Berachain, Injective Protocol, and others, Kava hosts a suite of numerous products and services and the native Tether USDT stablecoin atop its network.
- Stride - the premier Cosmos liquid staking protocol, Stride allows users to stake liquid staking asset stride tokens, or stTokens (such as stTIA, stATOM, and stINJ), while enabling on-chain participation of various DeFi primitives.
- Elys Network - a DeFi platform provisioning a hybrid AMM DEX featuring native USDC and multi-asset-index liquidity pools (LPs). Features seamless onboarding via its state-of-the-art wallet along with margin trading and interoperable multi-chain bridge connectivity.
In addition to the ecosystem partners listed above, Babylon also integrated its testnet (and its mainnet upon launch) with Terra Network, Agoric, XPLA, Archway, Secret Network, KYVE, Jackal Protocol, Persistence One, and others to realize a host of wide ranging utilities moving forward.
Babylon Roadmap and Future Initiatives
Babylon chain’s journey to this point has been eventful and not without a plethora of challenges.
From designing the protocol, to obtaining the desired funding, to building its own team, the Babylon project has accomplished a great deal in a short period of time and continues its march toward its all-encompassing goal: to safeguard the decentralized crypto economy via Proof of Stake infrastructure and the security guarantees of the Bitcoin network.
Since inception, Babylon has worked hard on the development of the project and its underlying infrastructure. Although Babylon is nearing the initial stages prior to launch, once its mainnet is live it will simply be a starting point to obtaining a vast user base and continued widespread adoption.
- May 2022 - Babylon chain is founded
- June 2023 - Babylon smart contracts and Bitcoin staking launch on pre-testnet
- October 2023 - Babylon announces its Bitcoin staking protocol MVP at Cosmoverse 2023
- December 2023 - Polychain Capital, Hack VC, and others finalize Babylon's Series A funding round
- Early 2023 to present - Babylon chain continues to announce integrations with various Cosmos chains
- February 2024 - Binance Labs invests an undisclosed sum in Babylon chain to bootstrap its continued development
- February 2024 - Babylon Bitcoin staking testnet launch
- April 2025 - Babylon chain mainnet launch
In addition, if you’d like to familiarize yourself with how Babylon was founded, what makes it special, and the differences between Proof of Work (like Bitcoin) and Proof of Stake systems, consider taking a deep dive into the first article in the series.

Babylon Chain Comparative Analysis
Though there are many staking and restaking platforms in the crypto industry with their own unique offerings, none so far have focused exclusively on Bitcoin the way Babylon has.
This construct represents a recalibration of what the Bitcoin network is capable of and is one of many in a long line of newly developed utilities for the Bitcoin network in the past 18 months, along with the recent additions of Ordinals NFTs, Layer 2 networks such as Stacks, and others.
The Babylon network makes use of cross-chain staking, a process that allows for the staking of remote crypto assets instead of or in addition to native PoS chain assets to enable a means to improve the underlying chain’s security by increasing the total market capitalization staked.
Cross-chain staking allows the staked foreign asset to remain on its own sovereign chain where it is locked in a staking contract designated for a highly desired validator on the chain it is securing. In this model, the staked asset is slashed only if the validator is guilty of slashable offenses.
This same idea is behind the mesh security concept proposed for the Cosmos ecosystem whereby the asset from one Cosmos appchain (the provider chain) can be cross-staked to secure another Cosmos appchain (the consumer chain).

Eigen Layer
The design discussed above is inspired by the ideation of EigenLayer’s Ethereum restaking paradigm. Although built to operate on the Ethereum blockchain and not focused on Bitcoin the way Babylon is, EigenLayer is the pioneer of the newly developed restaking DeFi niche.
As of this writing, EigenLayer has a total value locked (TVL) of over 12 billion. This is a remarkable figure considering the protocol has not yet fully launched on mainnet at this time. Because of the mega-success of EigenLayer, many believe that restaking has become the most prominent narrative of the 2024 and 2025 crypto bull run.
EigenLayer works by providing the larger infrastructure needed to fashion the interconnectivity of various independent restaking protocols that provide ether (ETH) restaking services atop its network via Ethereum. Essentially, users lock in their ETH tokens for a predetermined time frame in exchange for restaking tokens within a specific protocol (e.g., Lido’s stETH).
In return, the user is able to generate staking rewards for their ether and receive the restaking token in return (in this case stETH on Lido) which allows them participate in numerous DeFi primitives such as lending, borrowing, and yield farming.
EigenLayer also offers native ETH staking whereby a user must provide a minimum of 32 ETH (to run an Ethereum validator via an EigenPod) to participate via a mechanism where no liquid staking receipt tokens are provided in exchange.
Differently from Babylon Chain, EigenLayer makes use of an interconnect relationship with various middleware service providers called Actively Validated Services (AVSs). AVSs can include data availability (DA) layers, bridges, sidechains, oracle networks, trusted execution environments (TEEs), consensus protocols, threshold cryptography schemes, keeper networks, secure multi-party computation (MPC) frameworks, virtual machines, and more.
AVSs are used as a means to provide various network services atop the EigenLayer network (like the examples listed directly above) using a pooled security framework. This design greatly improves EigenLayer’s security and attack susceptibility because it dramatically increases the Cost-of-Corruption (the cost it takes to attack or take over the network) by a factor of 10 or more, therefore thwarting the efforts of potential attackers in the process.
Babylon’s cross-chain staking protocol represents a similar type of platform to the restaking primitive discussed above, albeit with two main differences compared to Cosmos mesh security-based chains and Ethereum restaking protocols: 1.) with Ethereum restaking and Cosmos mesh security protocols, the asset has been staked to the provider chain beforehand.
Conversely, Bitcoin is secured via PoW consensus rather than via the bitcoin asset itself, meaning the bitcoin asset is unencumbered and reduces the over-leveraged risks associated with restaking. And 2.) the Bitcoin network doesn’t implement stake slashing. Alternatively, Babylon optimizes the application of the Bitcoin scripting language and employs an advanced cryptographic mechanism to achieve the same end goal.
Despite these differences, EigenLayer is somewhat similar to Babylon with both offering strong products to their respective market segments.
If you want to learn more about Eigenlayer you should start with our introduction blog post: EigenLayer: A Restaking Protocol and On-Chain Collective

Ether.Fi
Ether.fi is a restaking protocol that piggybacks security from EigenLayer and Ethereum.
In a larger context, through EigenLayer, Ether.fi is able to connect with restaking protocols such as Lido Finance, Mantle Network (via mETH, Mantle itself is a Layer 2 blockchain), Swell Network, Rocket Pool, and others. Similarly to other Ethereum restaking protocols, Ether.fi allows protocol users to lock their ETH tokens within in exchange for restaked tokens (on Ether.fi these are known as eETH).
In return, the user is able to generate staking rewards for their ether and receive the eETH restaking token in exchange, allowing them to participate in DeFi utilities such as lending, borrowing, yield farming, and more.
One of the main characteristics that separates Ether.fi from many of its competitors is the fact that the platform claims to be the only existing protocol that allows users to control their own private keys at all times. This is particularly significant because it allows users to safeguard their ETH in the event of a hack, smart contract issue, larger protocol outage, node operator problem, or even if the permanent destruction of a protocol should occur.
On Ether.fi specifically, the user deposits their ETH within the protocol and are given eETH in return; while validators on the network are given a specialized NFT that helps the system create more revenue that is then shared with liquid stakers on the network.
In addition, Ether.fi has several main differences compared to Babylon chain:
- Ether.fi is built to operate by sharing security with Eigen Layer, Babylon is not
- Ether.fi and EigenLayer are Ethereum-specific instead of Bitcoin-based like Babylon
- the Ether.fi platform is more akin to a Cosmos consumer zone and not a larger infrastructure solution like Babylon or EigenLayer (both of which provide the staking and restaking platforms that chains like Ether.fi, Stride, and many others make use of)
In March of this year, Ether.fi launched as a Binance incubated project via the Binance Launchpool framework, Binance’s in-house token offering framework.
This event helped propel the Ether.fi platform to new heights and has helped increase its TVL to over 4 billion as of April 2024. This has really helped increase user onboarding numbers and trust in the platform over the last several weeks, cementing Ether.fi’s status as a reputable liquid staking protocol moving forward.

Stride
Unlike EigerLayer and Ether.fi, Stride is a zone (chain) and liquid staking protocol operating on the Cosmos network. Stride is one of a large number of Cosmos consumer zones that harnesses a robust integration with the Babylon platform.
Like many zones currently connected to Babylon chain, Babylon allows users to earn incentivized staking and liquid staking rewards in exchange for increased security guarantees on the Stride network. This is realized through a synergistic relationship with Babylon and the Bitcoin network which allows Stride to make use of Bitcoin security.
Similarly to Ether.fi, the Stride liquid staking protocol allows users to stake other Cosmos chain assets (think Cosmos’ ATOM, Celestia’s TIA, Osmosis’ OSMO, Injective’s INJ, and others) within the Stride protocol in exchange for liquid staking tokens. For example, if a user wishes to bond (stake) their TIA within Stride they in turn are given stTIA (or Stride liquid staked TIA) as a receipt token in return.
This token can then be used to participate in other forms of DeFi on Stride and acts as a proof of deposit that allows the users to unbond their original TIA at any time (like most liquid staking protocols, there is no time-based lock up to withdraw the initially deposited asset).
Through its connectivity with the Keplr wallet, the Osmosis DEX, and its proprietary liquid staking protocol, in recent months Stride has become one of the leading projects building on the Cosmos network and is arguably the most promising liquid staking platform within the Cosmos ecosystem.
Stride and other zones within the Cosmos ecosystem help provide a synergistic tri-tiered relationship between the larger Cosmos network, Babylon chain, and the Bitcoin blockchain. This interconnected paradigm compliments all parties equally, while rewarding users for their efforts in an security-focused, decentralized, and robust manner.
Centralized Crypto Staking and Custodial Providers
Centralized staking and custodial providers such as crypto exchanges, wallets, and the like, provide a means for users to earn incentivized yield, albeit with arguably much higher risks than traditional decentralized censorship-resistant platforms like Babylon.
When a centralized entity holds a user’s crypto on their behalf, they are putting their trust solely in the hands of a large commercial entity. If it's not obvious first hand, although unlikely, there is a chance that when a user locks up their tokens on a centralized platform, that they could lose their funds altogether or have them locked and inaccessible for various illegitimate reasons for a long period.
There have been many instances of this occurring in recent years, most notably during the 2022 bear market, including catastrophes that happened to the likes of Terra, Celsius Network, FTX, BlockFi, Three Arrows Capital, Voyager Digital, and others.
Although there are additional risks associated with decentralized staking platforms such as network outages, smart contract issues, and so on, protocols such as Babylon ensure user assets are not held by third-parties and are instead managed by user’s themselves.
Regulatory and Compliance Concerns
Because of the newly conceptualized idea behind Babylon chain and its unique first-of-kind design, it may be too soon to tell what kind of regulatory roadblocks, if any, the platform could be susceptible to moving forward.
The fact that the Bitcoin Spot ETF was accepted in January in the United States could bode well for Babylon because of the project’s integration with the world’s largest cryptocurrency and the lessened hardline stance against the crypto industry in the US of late.
That said, it could also be negative because of the fact that Babylon is connecting PoS chains to the Bitcoin network as a means to leverage the network’s security, while allowing investors to earn yield through PoS staking awards.
In the US, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has been reluctant to give staking service providers the benefit of the doubt, as is evidenced by past crackdowns, lawsuits, and fines levied towards centralized exchanges like Coinbse, Kraken, and others.
However, Babylon is not a centralized entity akin to the aforementioned exchanges, in fact Babylon is the exact opposite in many respects, but because these precedents have been set in the past, they could result in issues for the project although seemingly unlikely.
Moreover, it seems that politicians and judges in the US have more often than not sided with the companies being attacked in numerous lawsuits brought on by the SEC, often calling the SECs “regulation by enforcement” lackluster and unethical.
It seems that Babylon and others will continue to walk the tightrope of what is accepted and what is not in the US government-enforced system without proper regulatory guidelines in place. Let’s hope that these guidelines become clearer for all involved sooner rather than later.
Babylon Chain’s Long-Term Potential
Babylon chain and its underlying ecosystem represent a leading-edge framework focused on expanding the decentralized crypto economy.
Babylon’s offering as a middleware connectivity layer that enables secure, non-custodial, rapid staking of Bitcoin via various Proof of Stake blockchains is an innovation that is difficult to match in industry terms.
Although there are numerous staking and restaking protocols within the blockchain landscape, many believe there are few competitors that employ the same features and utility that Babylon offers, especially because of its connectivity to Bitcoin and its ability to share its security with a larger number of protocols in a simultaneous manner.
Babylon’s design, security, and interoperable nature surely stands out as the platform represents a solid solution to bring liquidity and continued adoption into the Cosmos ecosystem (and eventually others) long-term.
This may change in time, but it seems likely that for the foreseeable future Babylon will remain a first-of-kind game-changing solution that provides staking for the most censorship-resistant blockchain network and most scarce asset on the globe — bitcoin (BTC). The Babylon team strongly believes their project will help ignite a renaissance for the Bitcoin protocol and its underlying asset by increasing their utility moving forward.
Resources
The information provided by DAIC, including but not limited to research, analysis, data, or other content, is offered solely for informational purposes and does not constitute investment advice, financial advice, trading advice, or any other type of advice. DAIC does not recommend the purchase, sale, or holding of any cryptocurrency or other investment.


